Prospects of nanomaterials-enabled biosensors for COVID-19 detection
- PMID: 33254928
- PMCID: PMC7492839
- DOI: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.142363
Prospects of nanomaterials-enabled biosensors for COVID-19 detection
Abstract
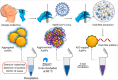
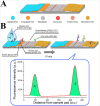
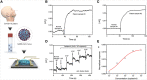
We are currently facing the COVID-19 pandemic which is the consequence of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus (SARS-CoV-2). Since no specific vaccines or drugs have been developed till date for the treatment of SARS-CoV-2 infection, early diagnosis is essential to further combat this pandemic. In this context, the reliable, rapid, and low-cost technique for SARS-CoV-2 diagnosis is the foremost priority. At present reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) is the reference technique presently being used for the detection of SARS-CoV-2 infection. However, in a number of cases, false results have been noticed in COVID-19 diagnosis. To develop advanced techniques, researchers are continuously working and in the series of constant efforts, nanomaterials-enabled biosensing approaches can be a hope to offer novel techniques that may perhaps meet the current demand of fast and early diagnosis of COVID-19 cases. This paper provides an overview of the COVID-19 pandemic and nanomaterials-enabled biosensing approaches that have been recently reported for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2. Though limited studies on the development of nanomaterials enabled biosensing techniques for the diagnosis of SARS-CoV-2 have been reported, this review summarizes nanomaterials mediated improved biosensing strategies and the possible mechanisms that may be responsible for the diagnosis of the COVID-19 disease. It is reviewed that nanomaterials e.g. gold nanostructures, lanthanide-doped polysterene nanoparticles (NPs), graphene and iron oxide NPs can be potentially used to develop advanced techniques offered by colorimetric, amperometric, impedimetric, fluorescence, and optomagnetic based biosensing of SARS-CoV-2. Finally, critical issues that are likely to accelerate the development of nanomaterials-enabled biosensing for SARS-CoV-2 infection have been discussed in detail. This review may serve as a guide for the development of advanced techniques for nanomaterials enabled biosensing to fulfill the present demand of low-cost, rapid and early diagnosis of COVID-19 infection.
Keywords: Biosensors; COVID-19; Coronavirus; Nanomaterials; SARS-CoV-2.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Authors of the manuscript declare there is no conflict of interests.
Figures




References
-
- Barnett J.M., Monnier B.M., Tyler S., West D., Ballantine-Dykes H., Regan E.…Luxton R. Initial trail results of a magnetic biosensor for the rapid detection of Porcine Reproductive and Respiratory Virus (PRRSV) infection. Sensing and Bio-Sensing Research. 2020;27 doi: 10.1016/j.sbsr.2019.100315. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

