Best Procedure for the Management of Common Bile Duct Stones via the Papilla: Literature Review and Analysis of Procedural Efficacy and Safety
- PMID: 33255554
- PMCID: PMC7760048
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9123808
Best Procedure for the Management of Common Bile Duct Stones via the Papilla: Literature Review and Analysis of Procedural Efficacy and Safety
Abstract
Background: Endoscopic management of common bile duct stones (CBDS) is standard; however, various techniques are performed via the papilla, and the best procedure in terms of both efficacy and safety has not been determined.
Methods: Endoscopic procedures were classified into five categories according to endoscopic sphincterotomy (EST) and balloon dilation (BD): (1) EST, (2) endoscopic papillary BD (≤10 mm) (EPBD), (3) EST followed by BD (≤10 mm) (ESBD), (4) endoscopic papillary large BD (≥12 mm) (EPLBD), and (5) EST followed by large BD (≥12 mm) (ESLBD). We performed a literature review of prospective and retrospective studies to compare efficacy and adverse events (AEs). Each procedure was associated with different efficacy and AE profiles.
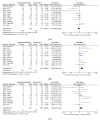
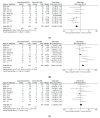
Results: In total, 19 prospective and seven retrospective studies with a total of 3930 patients were included in this study. For EST, the complete stone removal rate at the first session, rate of mechanical lithotripsy (ML), and rate of overall AEs in EST were superior to EPBD, but a higher rate of bleeding was found for EST. Based on one retrospective study, complete stone removal rate at the first session, rate of ML, and rate of overall AEs were superior for ESBD vs. EST, and the rate of bleeding for the former was also lower. Complete stone removal rate at the first session and rate of ML for ESLBD were superior to those for EST, with no significant difference in rate of AEs. For EST vs. EPLBD, complete stone removal rate at the first session and rate of ML were superior for the latter. For EPLBD vs. ESLBD, the efficacy and safety were similar.
Conclusions: ESBD is considered the best procedure for the management of small CBDS, but strong evidence is lacking. For large CBDS, both ESLBD and EPLBD are similar.
Keywords: bleeding; common bile duct stones; endoscopic papillary balloon dilation; endoscopic sphincterotomy; post-ERCP pancreatitis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
The efficacy of limited endoscopic sphincterotomy plus endoscopic papillary large balloon dilation for removal of large bile duct stones.BMC Gastroenterol. 2019 Jun 18;19(1):93. doi: 10.1186/s12876-019-1017-x. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 31215401 Free PMC article.
-
A Preliminary Comparison of Endoscopic Sphincterotomy, Endoscopic Papillary Large Balloon Dilation, and Combination of the Two in Endoscopic Choledocholithiasis Treatment.Med Sci Monit. 2015 Sep 3;21:2607-12. doi: 10.12659/MSM.894158. Med Sci Monit. 2015. PMID: 26334173 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Evaluation of the safety and efficacy of minimal endoscopic sphincterotomy followed by papillary balloon dilation for the removal of common bile duct stones.Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2020 Jul 21;26(6):344-50. doi: 10.4103/sjg.SJG_162_20. Online ahead of print. Saudi J Gastroenterol. 2020. PMID: 32719239 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic Papillary Large Balloon Dilation Versus Endoscopic Sphincterotomy for Treatment of Bile Duct Stones.Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2019 Jun;17(2):221-230. doi: 10.1007/s11938-019-00234-5. Curr Treat Options Gastroenterol. 2019. PMID: 30945095 Review.
-
Comparative efficacy of various endoscopic techniques for the treatment of common bile duct stones: a network meta-analysis.Gastrointest Endosc. 2018 Jan;87(1):43-57.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.gie.2017.07.038. Epub 2017 Jul 27. Gastrointest Endosc. 2018. PMID: 28756105 Review.
Cited by
-
Large balloon sphincteroplasty for CBD stone removal during acute cholangitis. Single center propensity-score matched cohort study.Surg Endosc. 2025 Feb;39(2):1077-1085. doi: 10.1007/s00464-024-11402-9. Epub 2024 Dec 17. Surg Endosc. 2025. PMID: 39690334
-
A novel non-slip banded balloon catheter for endoscopic sphincteroplasty: an ex vivo and in vivo pilot study.Sci Rep. 2023 Mar 10;13(1):4032. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-31206-6. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 36899107 Free PMC article.
-
Comparative efficacy of ciprofol and propofol in reducing respiratory depression during ERCP anesthesia: a randomized controlled trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Nov 8;24(1):404. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02791-4. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 39516741 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Minimal endoscopic sphincterotomy followed by papillary balloon dilation to relieve choledocholithiasis in a 6-year-old girl with hereditary spherocytosis.Clin J Gastroenterol. 2024 Aug;17(4):782-787. doi: 10.1007/s12328-024-01960-9. Epub 2024 Mar 22. Clin J Gastroenterol. 2024. PMID: 38517593
-
Clinical efficacy of laparoscopic cholecystectomy combined with endoscopic papillary balloon dilation in treatment of gallbladder stones with common bile duct stones: A retrospective study.World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024 Jun 27;16(6):1700-1708. doi: 10.4240/wjgs.v16.i6.1700. World J Gastrointest Surg. 2024. PMID: 38983353 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kawai K. Preliminary report on endoscopic papillotomy. J. Kyoto Pref. Univ. Med. 1973;82:353–355.
-
- Isayama H., Komatsu Y., Inoue Y., Toda N., Shiratori Y., Tsujino T., Yamada H., Saitou K., Kawabe T., Omata M. Preserved function of the Oddi sphincter after endoscopic papillary balloon dilation. Hepato-Gastroenterology. 2003;50:1787–1791. - PubMed
-
- Disario J.A., Freeman M.L., Bjorkman D.J., Macmathuna P., Petersen B.T., Jaffe P.E., Morales T.G., Hixson L.J., Sherman S., Lehman G.A., et al. Endoscopic balloon dilation compared with sphincterotomy for extraction of bile duct stones. Gastroenterology. 2004;127:1291–1299. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.07.017. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

