Biochemical and Histopathological Alterations in Different Tissues of Rats Due to Repeated Oral Dose Toxicity of Cymoxanil
- PMID: 33255611
- PMCID: PMC7760546
- DOI: 10.3390/ani10122205
Biochemical and Histopathological Alterations in Different Tissues of Rats Due to Repeated Oral Dose Toxicity of Cymoxanil
Abstract
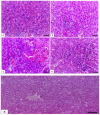
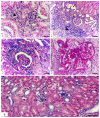
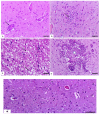
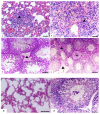
Evaluating potential adverse health impacts caused by pesticides is an important parameter in human toxicity. This study focuses on the importance of subchronic toxicity assessment of cymoxanil fungicide in rats with special reference to target biochemical enzymes and histopathological changes in different tissues. In this regard, a 21-day toxicity study with repeated cymoxanil oral doses was conducted. It has been shown that low doses (0.5 mg/kg) were less effective than medium (1 mg/kg) and high (2 mg/kg) doses. Moreover, high dose dose-treated rats showed piecemeal necrosis in the liver, interstitial nephritis and tubular degeneration in the kidneys, interstitial pneumonia and type II pneumocyte hyperplasia in the lungs, gliosis, spongiosis, and malacia in the brain, and testicular edema and degeneration in the testes. Cymoxanil significantly increased AST, ALT, and ALP in serum and liver, indicating tissue necrosis and possible leakage of these enzymes into the bloodstream. Creatinine levels increased, indicating renal damage. Similarly, significant inhibition was recorded in brain acetylcholinesterase, indicating that both synaptic transmission and nerve conduction were affected. Importantly, these histopathological and biochemical alterations were dose-dependent. Taken together, our study reported interesting biochemical and histopathological alterations in different rat tissues following repeated toxicity with oral doses of cymoxanil. Our study suggests future studies on different pesticides at different concentrations that would help urge governments to create more restrictive regulations concerning these compounds' levels.
Keywords: ALP; ALT; AST; brian; cholinesterase; cymoxanil; liver; rats; testes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest that can potentially influence the results of this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Repeated oral dose toxicity of iron oxide nanoparticles: biochemical and histopathological alterations in different tissues of rats.J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2012 Mar;12(3):2149-59. doi: 10.1166/jnn.2012.5796. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 2012. PMID: 22755032
-
Toxicity assessment of manganese oxide micro and nanoparticles in Wistar rats after 28 days of repeated oral exposure.J Appl Toxicol. 2013 Oct;33(10):1165-79. doi: 10.1002/jat.2887. Epub 2013 May 24. J Appl Toxicol. 2013. PMID: 23702825
-
Ameliorative effect of resveratrol against cymoxanil-mancozeb induced toxicity in rats.J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023 Jun;37(6):e23347. doi: 10.1002/jbt.23347. Epub 2023 Apr 3. J Biochem Mol Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37009748
-
Safety and nutritional assessment of GM plants and derived food and feed: the role of animal feeding trials.Food Chem Toxicol. 2008 Mar;46 Suppl 1:S2-70. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2008.02.008. Epub 2008 Feb 13. Food Chem Toxicol. 2008. PMID: 18328408 Review.
-
Total allowable concentrations of monomeric inorganic aluminum and hydrated aluminum silicates in drinking water.Crit Rev Toxicol. 2012 May;42(5):358-442. doi: 10.3109/10408444.2012.674101. Crit Rev Toxicol. 2012. PMID: 22512666 Review.
Cited by
-
In Silico Investigation of Selected Pesticides and Their Determination in Agricultural Products Using QuEChERS Methodology and HPLC-DAD.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Apr 28;24(9):8003. doi: 10.3390/ijms24098003. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37175728 Free PMC article.
-
Apis mellifera as a Model Species to Evaluate Toxicological Effects of Fungicides Used in Vineyard Agroecosystems.J Xenobiot. 2025 Jan 21;15(1):18. doi: 10.3390/jox15010018. J Xenobiot. 2025. PMID: 39997361 Free PMC article.
-
Ameliorative Effects of Bovine Lactoferrin on Benzene-Induced Hematotoxicity in Albino Rats.Front Vet Sci. 2022 Jun 22;9:907580. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2022.907580. eCollection 2022. Front Vet Sci. 2022. PMID: 35812844 Free PMC article.
-
Fertility protective effects of Brillantaisia patula leaf extract against cyclophosphamide-induced ovarian damage in Wistar rats.BMC Biotechnol. 2024 Nov 8;24(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s12896-024-00916-8. BMC Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39516799 Free PMC article.
-
Photocatalytic Detoxification of Some Insecticides in Aqueous Media Using TiO2 Nanocatalyst.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Sep 2;18(17):9278. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18179278. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34501865 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Álvarez-Martín A., Sánchez-Martín M.J., Pose-Juan E., Rodríguez-Cruz M.S. Effect of different rates of spent mushroom substrate on the dissipation and bioavailability of cymoxanil and tebuconazole in an agricultural soil. Sci. Total Environ. 2016;550:495–503. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.01.151. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

