Protective Effects of Fucoxanthin on High Glucose- and 4-Hydroxynonenal (4-HNE)-Induced Injury in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
- PMID: 33255669
- PMCID: PMC7760030
- DOI: 10.3390/antiox9121176
Protective Effects of Fucoxanthin on High Glucose- and 4-Hydroxynonenal (4-HNE)-Induced Injury in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells
Abstract
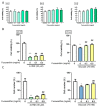
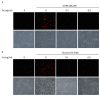
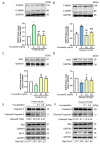
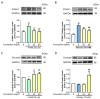
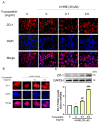
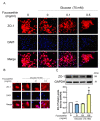
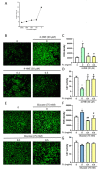
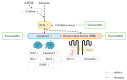
The incidence of diabetes mellitus is increasing due to the eating and living habits of modern people. As the disease progresses, the long-term effects of diabetes can cause microvascular disease, causing dysfunction in different parts of the body, which, in turn, leads to different complications, such as diabetic neuropathy, diabetic nephropathy, and diabetic retinopathy (DR). DR is the main cause of vision loss and blindness in diabetic patients. Persistent hyperglycemia may cause damage to the retina, induce the accumulation of inflammatory factors, and destroy the blood-retinal barrier function. Fucoxanthin (Fx) is a marine carotenoid extracted from seaweed. It accounts for more than 10% of the total carotenoids in nature. Fx is mainly found in brown algae and has strong antioxidant properties, due to its unique biologically active structure. This carotenoid also has the effects of reducing lipid peroxidation, reducing DNA damage, and preventing cardiovascular diseases as well as anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects. However, there is no relevant research on the protective effect of Fx in DR. Therefore, in this study, we explore the protective effect of Fx on the retina. Human retinal epithelial cells (ARPE-19) are used to investigate the protective effect of Fx on high glucose stress- (glucose 75 mM) and high lipid peroxidation stress (4-hydroxynonenal, 4-HNE (30 μM))-induced DR. The cell viability test shows that Fx recovered the cell damage, and Western blotting shows that Fx reduced the inflammation response and maintained the integrity of the blood-retinal barrier by reducing its apoptosis and cell adhesion factor protein expression. Using an antioxidant enzyme assay kit, we find that the protective effect of Fx may be related to the strong antioxidant properties of Fx, which increases catalase and reduces oxidative stress to produce a protective effect on the retina.
Keywords: antioxidant; fucoxanthin; retinopathy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Epigenomic, Transcriptomic, and Protective Effect of Carotenoid Fucoxanthin in High Glucose-Induced Oxidative Stress in Mes13 Kidney Mesangial Cells.Chem Res Toxicol. 2021 Mar 15;34(3):713-722. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.0c00235. Epub 2021 Jan 15. Chem Res Toxicol. 2021. PMID: 33448797
-
Protective Effects of Fucoxanthin on Hydrogen Peroxide-Induced Calcification of Heart Valve Interstitial Cells.Mar Drugs. 2021 May 26;19(6):307. doi: 10.3390/md19060307. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 34073219 Free PMC article.
-
Lutein reverses hyperglycemia-mediated blockage of Nrf2 translocation by modulating the activation of intracellular protein kinases in retinal pigment epithelial (ARPE-19) cells.J Cell Commun Signal. 2020 Jun;14(2):207-221. doi: 10.1007/s12079-019-00539-1. Epub 2019 Dec 9. J Cell Commun Signal. 2020. PMID: 31820335 Free PMC article.
-
Nutraceutical characteristics of the brown seaweed carotenoid fucoxanthin.Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020 Jun 15;686:108364. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2020.108364. Epub 2020 Apr 18. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2020. PMID: 32315653 Review.
-
Diabetic retinopathy pathogenesis and the ameliorating effects of melatonin; involvement of autophagy, inflammation and oxidative stress.Life Sci. 2018 Jan 15;193:20-33. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2017.12.001. Epub 2017 Dec 5. Life Sci. 2018. PMID: 29203148 Review.
Cited by
-
Diabetic retinopathy: Involved cells, biomarkers, and treatments.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Aug 9;13:953691. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.953691. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36016568 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fucoxanthin Suppresses Osteoclastogenesis via Modulation of MAP Kinase and Nrf2 Signaling.Mar Drugs. 2021 Feb 27;19(3):132. doi: 10.3390/md19030132. Mar Drugs. 2021. PMID: 33673704 Free PMC article.
-
The Regulation of the NF-κB p65 and Nrf2/HO-1 Signaling Pathways by Fucoxanthin in Human THP-1 Monocyte Macrophages Under a Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation Model.Foods. 2025 May 14;14(10):1746. doi: 10.3390/foods14101746. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40428524 Free PMC article.
-
Xanthophyll-Rich Extract of Phaeodactylum tricornutum Bohlin as New Photoprotective Cosmeceutical Agent: Safety and Efficacy Assessment on In Vitro Reconstructed Human Epidermis Model.Molecules. 2023 May 19;28(10):4190. doi: 10.3390/molecules28104190. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37241930 Free PMC article.
-
Through its genoprotective, mitochondrial bioenergetic modulation, and antioxidant effects, Fucoxanthin and its metabolite minimize Ochratoxin A-induced nephrotoxicity in HK-2 human kidney cells.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Jul 12;26(1):379. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04276-z. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40652198 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ram C., Jha A.K., Ghosh A., Gairola S., Syed A.M., Murty U.S., Naidu V.G.M., Sahu B.D. Targeting NLRP3 inflammasome as a promising approach for treatment of diabetic nephropathy: Preclinical evidences with therapeutic approaches. Eur. J Pharmacol. 2020;885:173503. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2020.173503. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Shukla U.V., Tripathy K. StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing; Treasure Island, FL, USA: 2020. Diabetic Retinopathy. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

