SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic Impact on Pediatric Emergency Rooms: A Multicenter Study
- PMID: 33255697
- PMCID: PMC7728065
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17238753
SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic Impact on Pediatric Emergency Rooms: A Multicenter Study
Abstract
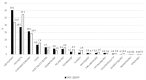
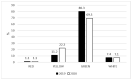
From 9 March to 3 May 2020, lockdown was declared in Italy due to the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) pandemic. Our aim was to evaluate how the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic and related preventive strategies affected pediatric emergency rooms (ERs) during this period. We performed a retrospective cohort multicenter study, comparing the lockdown period to the corresponding period in 2019. We examined 15 Italian pediatric ERs in terms of visit rates, specific diagnoses (grouped as air communicable diseases and non-air communicable diseases), and triage categories. During the lockdown period, ER admissions decreased by 81% compared to 2019 (52,364 vs. 10,112). All ER specific diagnoses decreased in 2020 and this reduction was significantly higher for air communicable diseases (25,462 vs. 2934, p < 0.001). Considering the triage category, red codes remained similar (1% vs. 1%), yellow codes increased (11.2% vs. 22.3%), and green codes decreased (80.3% vs. 69.5%). We can speculate that social distancing and simple hygiene measures drastically reduced the spread of air communicable diseases. The increase in yellow codes may have been related to a delay in primary care and, consequently, in ER admissions.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2; air communicable infections; emergency rooms; lockdown measures; pandemic; pediatric.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization WHO Director—General’s Openings Remarks at the Media Briefing on COVID-19. [(accessed on 28 October 2020)];2020 Mar 11; Available online: https://www.who.int/director-general/speeches/detail/who-director-genera....
-
- Istituto Superiore di Sanità Epicentro. Epidemia COVID-19. [(accessed on 23 November 2020)]; Available online: https://www.epicentro.iss.it/coronavirus/sars-cov-2-dashboard.
-
- Chan J.F.-W., Yuan S., Kok K.-H., To K.K.-W., Chu H., Yang J., Xing F., Liu J., Yip C.C.-Y., Poon R.W.-S., et al. A familial cluster of pneumonia associated with the 2019 novel coronavirus indicating person-to-person transmission: A study of a family cluster. Lancet. 2020;395:514–523. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30154-9. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous