Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Strategies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prevention: Emphasis on Secondary Prevention and Its Translational Challenges
- PMID: 33255794
- PMCID: PMC7760293
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9123817
Risk Factors, Pathogenesis, and Strategies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma Prevention: Emphasis on Secondary Prevention and Its Translational Challenges
Abstract
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is a leading cause of cancer-associated mortality globally. Given the limited therapeutic efficacy in advanced HCC, prevention of HCC carcinogenesis could serve as an effective strategy. Patients with chronic fibrosis due to viral or metabolic etiologies are at a high risk of developing HCC. Primary prevention seeks to eliminate cancer predisposing risk factors while tertiary prevention aims to prevent HCC recurrence. Secondary prevention targets patients with baseline chronic liver disease. Various epidemiological and experimental studies have identified candidates for secondary prevention-both etiology-specific and generic prevention strategies-including statins, aspirin, and anti-diabetic drugs. The introduction of multi-cell based omics analysis along with better characterization of the hepatic microenvironment will further facilitate the identification of targets for prevention. In this review, we will summarize HCC risk factors, pathogenesis, and discuss strategies of HCC prevention. We will focus on secondary prevention and also discuss current challenges in translating experimental work into clinical practice.
Keywords: NASH; chemoprevention; hepatitis; hepatocellular carcinoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Figures
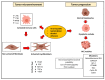


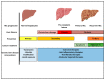

Similar articles
-
Generic chemoprevention of hepatocellular carcinoma.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019 Mar;1440(1):23-35. doi: 10.1111/nyas.13971. Epub 2018 Sep 17. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2019. PMID: 30221358 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Risk factors and prevention of hepatocellular carcinoma in the era of precision medicine.J Hepatol. 2018 Mar;68(3):526-549. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2017.09.016. Epub 2017 Oct 6. J Hepatol. 2018. PMID: 28989095 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prevention Strategies for Hepatocellular Carcinoma.2019 Aug 6. In: Hoshida Y, editor. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Translational Precision Medicine Approaches [Internet]. Cham (CH): Humana Press; 2019. Chapter 13. 2019 Aug 6. In: Hoshida Y, editor. Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Translational Precision Medicine Approaches [Internet]. Cham (CH): Humana Press; 2019. Chapter 13. PMID: 32078264 Free Books & Documents. Review.
-
Review article: the prevention of hepatitis B-related hepatocellular carcinoma.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Jul;48(1):5-14. doi: 10.1111/apt.14683. Epub 2018 May 3. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 29722445 Review.
-
Risk Factors and Prevention of Viral Hepatitis-Related Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Oncol. 2021 Sep 9;11:686962. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.686962. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34568017 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
HCC in the Era of Direct-Acting Antiviral Agents (DAAs): Surgical and Other Curative or Palliative Strategies in the Elderly.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Jun 17;13(12):3025. doi: 10.3390/cancers13123025. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34204186 Free PMC article.
-
Screening and interventions to prevent nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jan 14;29(2):286-309. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i2.286. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36687124 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hepatitis B Core Antibody Positivity Associated with Increased Risk of Liver Cancer in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C: Analysis of a Large Patient Cohort in Hawai'i.Hawaii J Health Soc Welf. 2022 May;81(5):127-133. Hawaii J Health Soc Welf. 2022. PMID: 35528754 Free PMC article.
-
Liquorice for pain?Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2021 Jul 16;11:20451253211024873. doi: 10.1177/20451253211024873. eCollection 2021. Ther Adv Psychopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34349979 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Echinacoside ameliorates hepatic fibrosis and tumor invasion in rats with thioacetamide-induced hepatocellular carcinoma.Biomol Biomed. 2024 Sep 6;24(5):1186-1198. doi: 10.17305/bb.2024.10367. Biomol Biomed. 2024. PMID: 38461536 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

