A Polyol-Polyol Super-Carbon-Chain Compound Containing Thirty-Six Carbon Stereocenters from the Dinoflagellate Amphidinium gibbosum: Absolute Configuration and Multi-Segment Modification
- PMID: 33255887
- PMCID: PMC7759953
- DOI: 10.3390/md18120590
A Polyol-Polyol Super-Carbon-Chain Compound Containing Thirty-Six Carbon Stereocenters from the Dinoflagellate Amphidinium gibbosum: Absolute Configuration and Multi-Segment Modification
Abstract
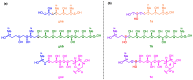
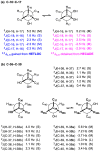
A super-carbon-chain compound, named gibbosol C, featuring a polyoxygenated C70-linear-carbon-chain backbone encompassing two acyclic polyol chains, was obtained from the South China Sea dinoflagellate Amphidinium gibbosum. Its planar structure was elucidated by extensive NMR investigations, whereas its absolute configurations, featuring the presence of 36 carbon stereocenters and 30 hydroxy groups, were successfully established by comparison of NMR data of the ozonolyzed products with those of gibbosol A, combined with J-based configuration analysis, Kishi's universal NMR database, and the modified Mosher's MTPA ester method. Multi-segment modification was revealed as the smart biosynthetic strategy for the dinoflagellate to create remarkable super-carbon-chain compounds with structural diversity.
Keywords: Amphidinium gibbosum; absolute configuration; marine dinoflagellate; multi-segment modification; super-carbon-chain compound.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Discovery of benthol A and its challenging stereochemical assignment: opening up a new window for skeletal diversity of super-carbon-chain compounds.Chem Sci. 2021 Jun 30;12(30):10197-10206. doi: 10.1039/d1sc02810c. eCollection 2021 Aug 4. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34447528 Free PMC article.
-
Determination of the Absolute Configuration of Super-Carbon-Chain Compounds by a Combined Chemical, Spectroscopic, and Computational Approach: Gibbosols A and B.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020 Jul 27;59(31):13028-13036. doi: 10.1002/anie.202004358. Epub 2020 Jun 3. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2020. PMID: 32343023
-
Amphirionin-2, a novel linear polyketide with potent cytotoxic activity from a marine dinoflagellate Amphidinium species.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Feb 1;25(3):635-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2014.12.003. Epub 2014 Dec 8. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 25534608
-
Bioactive secondary metabolites from symbiotic marine dinoflagellates: symbiodinolide and durinskiols.Chem Rec. 2010 Apr;10(2):57-69. doi: 10.1002/tcr.200900007. Chem Rec. 2010. PMID: 20333719 Review.
-
Marine huge molecules: the longest carbon chains in natural products.Chem Rec. 2010 Mar;10(1):48-52. doi: 10.1002/tcr.200900030. Chem Rec. 2010. PMID: 20143381 Review.
Cited by
-
The Chemistry of Phytoplankton.Chem Rev. 2024 Dec 11;124(23):13099-13177. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.4c00177. Epub 2024 Nov 21. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 39571071 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bioactive Polyketides from Amphidinium spp.: An In-Depth Review of Biosynthesis, Applications, and Current Research Trends.Mar Drugs. 2025 Jun 16;23(6):255. doi: 10.3390/md23060255. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40559664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery of benthol A and its challenging stereochemical assignment: opening up a new window for skeletal diversity of super-carbon-chain compounds.Chem Sci. 2021 Jun 30;12(30):10197-10206. doi: 10.1039/d1sc02810c. eCollection 2021 Aug 4. Chem Sci. 2021. PMID: 34447528 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kobayashi J., Ishibashi M. Bioactive metabolites of symbiotic marine microorganisms. Chem. Rev. 1993;93:1753–1769. doi: 10.1021/cr00021a005. - DOI
-
- Satake M., Murata M., Yasumoto T., Fujita T., Naoki H. Amphidinol, a polyhydroxypolyene antifungal agent with an unprecedented structure, from a marine dinoflagellate, Ampbidnium klebsii. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1991;113:9859–9861. doi: 10.1021/ja00026a027. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

