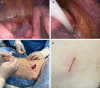
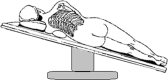
Tubeless uniportal thoracoscopic wedge resection with modified air leak test and chest tube drainage
- PMID: 33256711
- PMCID: PMC7706205
- DOI: 10.1186/s12893-020-00910-9
Tubeless uniportal thoracoscopic wedge resection with modified air leak test and chest tube drainage
Abstract
Background: To investigate whether tubeless uniportal thoracoscopic wedge resection with modified air leak test and chest tube drainage has better short-term outcomes than non-intubated approach with chest tube drainage.
Methods: Data were collected retrospectively from January 2017 and December 2019. Tubeless group included 55 patients with pulmonary nodules underwent tubeless uniportal thoracoscopic wedge resection, 211 patients underwent non-intubated uniportal thoracoscopic wedge resection with chest tube drainage were included in drainage group. Peri-operative outcomes between two groups were compared.
Results: After 1:1 matching, 110 patients remained for analysis, baseline demographic and clinical variables were comparable between the two groups. Mean incision size was 3 cm in both group. Mean operative time was 59.3 min in tubeless group and 52.8 min in drainage group. The detectable mean lowest SpO2 and mean peak EtCO2 during operation was acceptable in both groups. Conversion to intubated ventilation or thoracotomy was not required. No patient failed the air leak test and did not undergo a tubeless procedure. Mean postoperative hospital stay was 1.5 days in tubeless group and 2.5 days in drainage group. Residual pneumothorax or subcutaneous emphysema was not frequent and mild in tubeless group. Side effects were rare and mild, including cough and hemoptysis. No re-intervention or readmission occurred. The postoperative VAS score was significantly lower in tubeless group.
Conclusions: Tubeless uniportal thoracoscopic wedge resection with modified air leak test and chest tube drainage is feasible and safe for selected patients with peripheral pulmonary nodules, it might reduce post-operation pain and lead to faster recovery.
Keywords: Non-intubated; Thoracoscopic; Tubeless; Uniportal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Tubeless Uniportal Thoracoscopic Wedge Resection for Peripheral Lung Nodules.Ann Thorac Surg. 2017 Feb;103(2):462-468. doi: 10.1016/j.athoracsur.2016.09.006. Epub 2016 Nov 16. Ann Thorac Surg. 2017. PMID: 27865474
-
Is tubeless uniportal video-assisted thoracic surgery for pulmonary wedge resection a safe procedure?Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2020 Aug 1;58(Suppl_1):i70-i76. doi: 10.1093/ejcts/ezaa061. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2020. PMID: 32182334
-
Early chest tube removal after video-assisted thoracoscopic wedge resection of the lung.Ann Thorac Surg. 1998 Nov;66(5):1751-4. doi: 10.1016/s0003-4975(98)00946-1. Ann Thorac Surg. 1998. PMID: 9875783
-
In minor and major thoracic procedures is uniport superior to multiport video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery?Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015 Apr;20(4):550-5. doi: 10.1093/icvts/ivu375. Epub 2015 Jan 28. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2015. PMID: 25634778 Review.
-
Risk of Pneumothorax Requiring Pleural Drainage after Drainless VATS Pulmonary Wedge Resection: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Innovations (Phila). 2022 Jan-Feb;17(1):14-24. doi: 10.1177/15569845221074431. Innovations (Phila). 2022. PMID: 35225064
Cited by
-
The Anesthesiologist's Perspective Regarding Non-intubated Thoracic Surgery: A Scoping Review.Front Surg. 2022 Apr 4;9:868287. doi: 10.3389/fsurg.2022.868287. eCollection 2022. Front Surg. 2022. PMID: 35445075 Free PMC article.
-
Uniportal video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery without drainage-tube placement for pulmonary wedge resection: a single-center retrospective study.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2022 Dec 17;17(1):317. doi: 10.1186/s13019-022-02053-9. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2022. PMID: 36527034 Free PMC article.
-
SV-VATS exhibits dual intraoperative and postoperative advantages.Ann Transl Med. 2021 Jun;9(12):970. doi: 10.21037/atm-21-2297. Ann Transl Med. 2021. PMID: 34277770 Free PMC article.
-
Chest tube-free video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery secured by quantitative air leak monitoring: a case series.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Jan 31;15(1):146-154. doi: 10.21037/jtd-22-1749. Epub 2023 Jan 9. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 36794133 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of perioperative outcomes with or without routine chest tube drainage after video-assisted thoracoscopic pulmonary resection: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Front Oncol. 2022 Aug 8;12:915020. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.915020. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36003771 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

