Genetic and epigenetic modification of human primary NK cells for enhanced antitumor activity
- PMID: 33256913
- PMCID: PMC7809645
- DOI: 10.1053/j.seminhematol.2020.11.006
Genetic and epigenetic modification of human primary NK cells for enhanced antitumor activity
Abstract
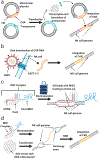
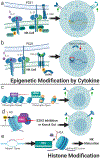
Cancer immunotherapy using genetically modified immune cells such as those expressing chimeric antigen receptors has shown dramatic outcomes in patients with refractory and relapsed malignancies. Natural killer (NK) cells as a member of the innate immune system, possessing both anticancer (cytotoxic) and proinflammatory (cytokine) responses to cancers and rare off-target toxicities have great potential for a wide range of cancer therapeutic settings. Therefore, improving NK cell antitumor activity through genetic modification is of high interest in the field of cancer immunotherapy. However, gene manipulation in primary NK cells has been challenging because of broad resistance to many genetic modification methods that work well in T cells. Here we review recent successful approaches for genetic and epigenetic modification of NK cells including epigenetic remodeling, transposons, mRNA-mediated gene delivery, lentiviruses, and CRISPR gene targeting.
Keywords: CRISPR; Cancer immunotherapy; Genetic modification; Natural killer cells; Transposons; Viral vectors.
Copyright © 2020 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest Dean Lee- Kiadis Pharma- Scientific Advisory Board, Stock, Consulting, IP licensing. Caribou Biosciences- Scientific Advisory Board. Courier Therapeutics- Scientific Advisory Board, Stock.
Figures

References
-
- Seillet C, Belz GT. Assessment of Gene Function of Mouse Innate Lymphoid Cells for In Vivo Analysis Using Retroviral Transduction In: Moll J, Carotta S, editors. Target Identification and Validation in Drug Discovery: Methods and Protocols, Methods in Molecular Biology. 1953: Springer Science+Business Media, LLC, part of Springer Nature; 2019. p. 231–40. - PubMed
-
- Lin C, Zhang J. Chimeric antigen receptor engineered innate immune cells in cancer immunotherapy. Sci China Life Sci. 2019;62(5):633–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

