Loneliness during a strict lockdown: Trajectories and predictors during the COVID-19 pandemic in 38,217 United Kingdom adults
- PMID: 33257177
- PMCID: PMC7768183
- DOI: 10.1016/j.socscimed.2020.113521
Loneliness during a strict lockdown: Trajectories and predictors during the COVID-19 pandemic in 38,217 United Kingdom adults
Abstract
Rationale: There are increasing worries that lockdowns and 'stay-at-home' orders due to the COVID-19 pandemic could lead to a rise in loneliness, which is recognised as a major public health concern. But profiles of loneliness during the pandemic and risk factors remain unclear.
Objective: The current study aimed to examine if and how loneliness levels changed during the strict lockdown and to explore the clustering of loneliness growth trajectories.
Methods: Data from 38,217 UK adults in the UCL COVID -19 Social Study (a panel study collecting data weekly during the pandemic) were analysed during the strict lockdown period in the UK (23/03/2020-10/05/2020). The sample was well-stratified and weighted to population proportions of gender, age, ethnicity, education and geographical location. Growth mixture modelling was used to identify the latent classes of loneliness growth trajectories and their predictors.
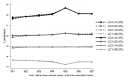
Results: Analyses revealed four classes, with the baseline loneliness level ranging from low to high. In the first a few weeks of lockdown, loneliness levels increased in the highest loneliness group, decreased in the lowest loneliness group, and stayed relatively constant in the middle two groups. Younger adults (OR = 2.17-6.81), women (OR = 1.59), people with low income (OR = 1.3), the economically inactive (OR = 1.3-2.04) and people with mental health conditions (OR = 5.32) were more likely to be in highest loneliness class relative to the lowest. Further, living with others or in a rural area, and having more close friends or greater social support were protective.
Conclusions: Perceived levels of loneliness under strict lockdown measures due to COVID-19 were relatively stable in the UK, but for many people these levels were high with no signs of improvement. Results suggest that more efforts are needed to address loneliness.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Lockdown; Loneliness; Longitudinal; Mental health; Social factor; Trajectory.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures
Comment in
-
Evidence-informed and targeted public health interventions are required to reduce the broader behavioural health impact of loneliness and social isolation due to the COVID-19 pandemic.Evid Based Nurs. 2022 Apr;25(2):63. doi: 10.1136/ebnurs-2020-103384. Epub 2021 Aug 9. Evid Based Nurs. 2022. PMID: 34373317 No abstract available.
References
-
- Baker Z.G., Krieger H., Leroy A.S. Fear of missing out: relationships with depression, mindfulness, and physical symptoms. Translational Issues in Psychological Science. 2016;2:275.
-
- Boss L., Kang D.-H., Branson S. Loneliness and cognitive function in the older adult: a systematic review. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2015;27:541. - PubMed
-
- Brodeur A., Clark A.E., Fleche S., Powdthavee N. 2020. Assessing the Impact of the Coronavirus Lockdown on Unhappiness, Loneliness, and Boredom Using Google Trends. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.12129.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical