Stress and the dopaminergic reward system
- PMID: 33257725
- PMCID: PMC8080624
- DOI: 10.1038/s12276-020-00532-4
Stress and the dopaminergic reward system
Abstract
Dopamine regulates reward-related behavior through the mesolimbic dopaminergic pathway. Stress affects dopamine levels and dopaminergic neuronal activity in the mesolimbic dopamine system. Changes in mesolimbic dopaminergic neurotransmission are important for coping with stress, as they allow adaption to behavioral responses to various environmental stimuli. Upon stress exposure, modulation of the dopaminergic reward system is necessary for monitoring and selecting the optimal process for coping with stressful situations. Aversive stressful events may negatively regulate the dopaminergic reward system, perturbing reward sensitivity, which is closely associated with chronic stress-induced depression. The mesolimbic dopamine system is excited not only by reward but also by aversive stressful stimuli, which adds further intriguing complexity to the relationship between stress and the reward system. This review focuses on lines of evidence related to how stress, especially chronic stress, affects the mesolimbic dopamine system, and discusses the role of the dopaminergic reward system in chronic stress-induced depression.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Figures

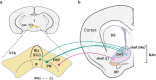
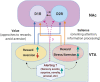
References
-
- Selye H. A Syndrome produced by diverse nocuous agents. Nature. 1936;138:32. - PubMed
-
- Selye H. The evolution of the stress concept. Am. Sci. 1973;61:692–699. - PubMed
-
- McEwen BS. Stress, adaptation, and disease. Allostasis and allostatic load. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1998;840:33–44. - PubMed
-
- Hammen C. Stress and depression. Ann. Rev. Clin. Psychol. 2005;1:293–319. - PubMed
-
- Pani L, Porcella A, Gessa G. The role of stress in the pathophysiology of the dopaminergic system. Mol. Psychiatry. 2000;5:14–21. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2016M3A9D5A01952412/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- 2013M3A9D5072550/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- 2017R1A2B4008875/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- 2015R1A5A1009024/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
- 2020R1A2C2101010/National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

