RON signalling promotes therapeutic resistance in ESR1 mutant breast cancer
- PMID: 33257837
- PMCID: PMC7782501
- DOI: 10.1038/s41416-020-01174-z
RON signalling promotes therapeutic resistance in ESR1 mutant breast cancer
Abstract
Background: Oestrogen Receptor 1 (ESR1) mutations are frequently acquired in oestrogen receptor (ER)-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC) patients who were treated with aromatase inhibitors (AI) in the metastatic setting. Acquired ESR1 mutations are associated with poor prognosis and there is a lack of effective therapies that selectively target these cancers.
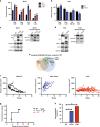
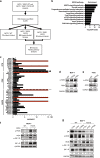
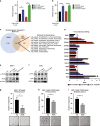
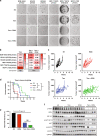
Methods: We performed a proteomic kinome analysis in ESR1 Y537S mutant cells to identify hyperactivated kinases in ESR1 mutant cells. We validated Recepteur d'Origine Nantais (RON) and PI3K hyperactivity through phospho-immunoblot analysis, organoid growth assays, and in an in vivo patient-derived xenograft (PDX) metastatic model.
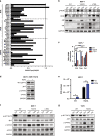
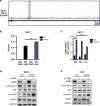
Results: We demonstrated that RON was hyperactivated in ESR1 mutant models, and in acquired palbociclib-resistant (PalbR) models. RON and insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor (IGF-1R) interacted as shown through pharmacological and genetic inhibition and were regulated by the mutant ER as demonstrated by reduced phospho-protein expression with endocrine therapies (ET). We show that ET in combination with a RON inhibitor (RONi) decreased ex vivo organoid growth of ESR1 mutant models, and as a monotherapy in PalbR models, demonstrating its therapeutic efficacy. Significantly, ET in combination with the RONi reduced metastasis of an ESR1 Y537S mutant PDX model.
Conclusions: Our results demonstrate that RON/PI3K pathway inhibition may be an effective treatment strategy in ESR1 mutant and PalbR MBC patients. Clinically our data predict that ET resistance mechanisms can also contribute to CDK4/6 inhibitor resistance.
Conflict of interest statement
ALW previously received research support from Aslan Pharmaceuticals. SAWF is a Subject Editor, member of the Editorial Board of BJC and Guest Editor of the Special Issue on Metastasis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Oral Estrogen Receptor PROTAC Vepdegestrant (ARV-471) Is Highly Efficacious as Monotherapy and in Combination with CDK4/6 or PI3K/mTOR Pathway Inhibitors in Preclinical ER+ Breast Cancer Models.Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Aug 15;30(16):3549-3563. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-23-3465. Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38819400 Free PMC article.
-
Preclinical Efficacy of Ron Kinase Inhibitors Alone and in Combination with PI3K Inhibitors for Treatment of sfRon-Expressing Breast Cancer Patient-Derived Xenografts.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Dec 15;21(24):5588-600. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-3283. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26289070 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of SERD/SERM Hybrid-CDK4/6 Inhibitor Combinations in Models of Endocrine Therapy-Resistant Breast Cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2015 Nov 15;21(22):5121-5130. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0360. Epub 2015 May 19. Clin Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25991817 Free PMC article.
-
ESR1 mutation as an emerging clinical biomarker in metastatic hormone receptor-positive breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2021 Aug 15;23(1):85. doi: 10.1186/s13058-021-01462-3. Breast Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34392831 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ESR1 mutations and therapeutic resistance in metastatic breast cancer: progress and remaining challenges.Br J Cancer. 2022 Feb;126(2):174-186. doi: 10.1038/s41416-021-01564-x. Epub 2021 Oct 7. Br J Cancer. 2022. PMID: 34621045 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An immune-humanized patient-derived xenograft model of estrogen-independent, hormone receptor positive metastatic breast cancer.Breast Cancer Res. 2021 Oct 30;23(1):100. doi: 10.1186/s13058-021-01476-x. Breast Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34717714 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of modules and key genes associated with breast cancer subtypes through network analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 May 29;14(1):12350. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-61908-4. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38811600 Free PMC article.
-
Proteomic profiling reveals that ESR1 mutations enhance cyclin-dependent kinase signaling.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 22;14(1):6873. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-56412-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38519482 Free PMC article.
-
An Introduction and Overview of RON Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Signaling.Genes (Basel). 2023 Feb 17;14(2):517. doi: 10.3390/genes14020517. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36833444 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Mesenchymal Markers in Colorectal Cancer Metastasis.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 Jul 4;52(1):673. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10745-3. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40613936 Review.
References
-
- (WHO) IAfRoCIaWHO. GLOBOCAN 2018: Breast 2019. http://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/20-Breast-fact-sheet.pdf. (2018)
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative G. Effects of chemotherapy and hormonal therapy for early breast cancer on recurrence and 15-year survival: an overview of the randomised trials. Lancet. 365, 1687–1717 (2005). - PubMed
-
- Zhang QX, Borg A, Wolf DM, Oesterreich S, Fuqua SA. An estrogen receptor mutant with strong hormone-independent activity from a metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1997;57:1244–1249. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- PDF12230127/Susan G. Komen (Susan G. Komen Breast Cancer Foundation)
- T322389301302/U.S. Department of Health & Human Services | National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- 19-055/Breast Cancer Research Foundation (BCRF)
- RR140033/Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas)
- P30 CA125123/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA166422/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RP180712/Cancer Prevention and Research Institute of Texas (Cancer Prevention Research Institute of Texas)
- T32 CA203690/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA072038/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA207270/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM008231/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

