The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 33257900
- PMCID: PMC8557973
- DOI: 10.1038/s41590-020-00816-x
The immunology of rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
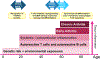
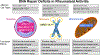
The immunopathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) spans decades, beginning with the production of autoantibodies against post-translationally modified proteins (checkpoint 1). After years of asymptomatic autoimmunity and progressive immune system remodeling, tissue tolerance erodes and joint inflammation ensues as tissue-invasive effector T cells emerge and protective joint-resident macrophages fail (checkpoint 2). The transition of synovial stromal cells into autoaggressive effector cells converts synovitis from acute to chronic destructive (checkpoint 3). The loss of T cell tolerance derives from defective DNA repair, causing abnormal cell cycle dynamics, telomere fragility and instability of mitochondrial DNA. Mitochondrial and lysosomal anomalies culminate in the generation of short-lived tissue-invasive effector T cells. This differentiation defect builds on a metabolic platform that shunts glucose away from energy generation toward the cell building and motility programs. The next frontier in RA is the development of curative interventions, for example, reprogramming T cell defects during the period of asymptomatic autoimmunity.
Figures

References
-
- Mahler M, Martinez-Prat L, Sparks JA & Deane KD Precision medicine in the care of rheumatoid arthritis: Focus on prediction and prevention of future clinically-apparent disease. Autoimmun Rev 19, 102506 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Alarcon GS Epidemiology of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 21, 589–604 (1995). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

