Time course of phosphorylated-tau181 in blood across the Alzheimer's disease spectrum
- PMID: 33257949
- PMCID: PMC7880671
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awaa399
Time course of phosphorylated-tau181 in blood across the Alzheimer's disease spectrum
Erratum in
-
Erratum to: Time course of phosphorylated-tau181 in blood across the Alzheimer's disease spectrum.Brain. 2021 Jul 28;144(6):e57. doi: 10.1093/brain/awab075. Brain. 2021. PMID: 33876218 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
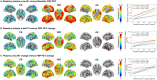
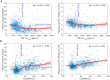
Tau phosphorylated at threonine 181 (p-tau181) measured in blood plasma has recently been proposed as an accessible, scalable, and highly specific biomarker for Alzheimer's disease. Longitudinal studies, however, investigating the temporal dynamics of this novel biomarker are lacking. It is therefore unclear when in the disease process plasma p-tau181 increases above physiological levels and how it relates to the spatiotemporal progression of Alzheimer's disease characteristic pathologies. We aimed to establish the natural time course of plasma p-tau181 across the sporadic Alzheimer's disease spectrum in comparison to those of established imaging and fluid-derived biomarkers of Alzheimer's disease. We examined longitudinal data from a large prospective cohort of elderly individuals enrolled in the Alzheimer's Disease Neuroimaging Initiative (ADNI) (n = 1067) covering a wide clinical spectrum from normal cognition to dementia, and with measures of plasma p-tau181 and an 18F-florbetapir amyloid-β PET scan at baseline. A subset of participants (n = 864) also had measures of amyloid-β1-42 and p-tau181 levels in CSF, and another subset (n = 298) had undergone an 18F-flortaucipir tau PET scan 6 years later. We performed brain-wide analyses to investigate the associations of plasma p-tau181 baseline levels and longitudinal change with progression of regional amyloid-β pathology and tau burden 6 years later, and estimated the time course of changes in plasma p-tau181 and other Alzheimer's disease biomarkers using a previously developed method for the construction of long-term biomarker temporal trajectories using shorter-term longitudinal data. Smoothing splines demonstrated that earliest plasma p-tau181 changes occurred even before amyloid-β markers reached abnormal levels, with greater rates of change correlating with increased amyloid-β pathology. Voxel-wise PET analyses yielded relatively weak, yet significant, associations of plasma p-tau181 with amyloid-β pathology in early accumulating brain regions in cognitively healthy individuals, while the strongest associations with amyloid-β were observed in late accumulating regions in patients with mild cognitive impairment. Cross-sectional and particularly longitudinal measures of plasma p-tau181 were associated with widespread cortical tau aggregation 6 years later, covering temporoparietal regions typical for neurofibrillary tangle distribution in Alzheimer's disease. Finally, we estimated that plasma p-tau181 reaches abnormal levels ∼6.5 and 5.7 years after CSF and PET measures of amyloid-β, respectively, following similar dynamics as CSF p-tau181. Our findings suggest that plasma p-tau181 increases are associated with the presence of widespread cortical amyloid-β pathology and with prospective Alzheimer's disease typical tau aggregation, providing clear implications for the use of this novel blood biomarker as a diagnostic and screening tool for Alzheimer's disease.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; blood biomarkers; cerebrospinal fluid; positron emission tomography; tau.
© The Author(s) (2020). Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Guarantors of Brain.
Figures




Comment in
-
Concatenating plasma p-tau to Alzheimer's disease.Brain. 2021 Feb 12;144(1):14-17. doi: 10.1093/brain/awaa422. Brain. 2021. PMID: 33578422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baek MS, Cho H, Lee HS, Choi JY, Lee JH, Ryu YH, et al.Temporal trajectories of in vivo tau and amyloid-beta accumulation in Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2020; 47: 2879–86. - PubMed

