SarA plays a predominant role in controlling the production of extracellular proteases in the diverse clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus LAC and UAMS-1
- PMID: 33258416
- PMCID: PMC7738309
- DOI: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1855923
SarA plays a predominant role in controlling the production of extracellular proteases in the diverse clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus LAC and UAMS-1
Abstract
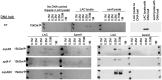
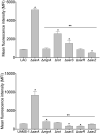
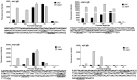
Using DNA affinity chromatography we demonstrate that the S. aureus regulatory proteins MgrA, Rot, SarA, and SarS bind DNA baits derived from the promoter regions associated with the genes encoding aureolysin, ScpAB, SspABC, and SplA-F. Three of four baits also bound SarR and SarZ, the exception in both cases being the ScpAB-associated bait. Using the USA300, methicillin-resistant strain LAC and the USA200, methicillin-sensitive strain UAMS-1, we generated mutations in the genes encoding each of these proteins alone and in combination with sarA and examined the impact on protease production, the accumulation of high molecular weight proteins, and biofilm formation. These studies confirmed that multiple regulatory loci are involved in limiting protease production to a degree that impacts all of these phenotypes, but also demonstrate that sarA plays a predominant role in this regard. Using sarA mutants unable to produce individual proteases alone and in combination with each other, we also demonstrate that the increased production of aureolysin and ScpA is particularly important in defining the biofilm-deficient phenotype of LAC and UAMS-1 sarA mutants, while aureolysin alone plays a key role in defining the reduced accumulation of alpha toxin and overall cytotoxicity as assessed using both osteoblasts and osteoclasts.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; mgrA; rot; sarA; sarR; sarS; sarZ; biofilm; extracellular protease; regulation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures










References
-
- Lowy FD. Staphylococcus aureus infections. N Engl J Med. 1998;339:520–532. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
