Leishmaniasis and phlebotomine sand flies in Oman Sultanate
- PMID: 33258444
- PMCID: PMC7708229
- DOI: 10.1051/parasite/2020064
Leishmaniasis and phlebotomine sand flies in Oman Sultanate
Abstract
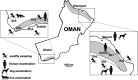
There are few data on leishmaniases and sandflies in Oman Sultanate. We carried out an eco-epidemiological study in 1998 in the two main mountains of the country, the Sharqiyah and the Dhofar. This study allowed us to isolate and identify three Leishmania strains from patients exhibiting cutaneous leishmaniasis. The typing carried out by isoenzymatic study and by molecular biology were congruent: two strains of Leishmania donovani zymodeme (Z) MON-31 isolated in the Sharqiyah and one L. tropica ZROM102 (ZMON-39 variant for 4 isoenzymes) from the Dhofar. No strain was isolated from canids. The study of sandflies identified 14 species distributed in the genera Phlebotomus, Sergentomyia and Grassomyia: Ph. papatasi, Ph. bergeroti, Ph. duboscqi, Ph. alexandri, Ph. saevus, Ph. sergenti, Se. fallax, Se. baghdadis, Se. cincta, Se. christophersi, Se. clydei, Se. tiberiadis, Se. africana, and Gr. dreyfussi. In Sharqiyah, the only candidate for the transmission of L. donovani was Ph. alexandri, but the low densities observed of this species do not argue in favor of any role. In Dhofar, Ph. sergenti is the most important proven vector of L. tropica, but Ph. saevus, a locally much more abundant species, constitutes a good candidate for transmission.
Title: Leishmanioses et phlébotomes au Sultanat d’Oman.
Abstract: Il existe peu de données sur les leishmanioses et les phlébotomes en Oman. Nous y avons mené en 1998 une étude éco-épidémiologique dans les deux principaux massifs montagneux du pays, la Sharqiyah et le Dhofar. Cette étude nous a permis d’isoler et d’identifier trois souches de Leishmania à partir de patients présentant des leishmanioses cutanées. Les typages menés par étude isoenzymatique et par biologie moléculaire ont été congruents : deux souches de Leishmania donovani ZMON-31 isolées dans la Sharqiyah et une de L. tropica ZROM102 (ZMON-39 variant pour 4 isoenzymes) originaire du Dhofar. Aucune souche n’a été isolée à partir de Canidés. L’étude des Phlébotomes a permis d’identifier 14 espèces réparties dans les genres Phlebotomus, Sergentomyia et Grassomyia : Ph. papatasi, Ph. bergeroti, Ph. duboscqi, Ph. alexandri, Ph. saevus, Ph. sergenti, Se. fallax, Se. baghdadis, Se. cincta, Se. christophersi, Se. clydei, Se. tiberiadis, Se. africana et Gr. dreyfussi. Dans la Sharqiyah, la seule espèce candidate à la transmission de L. donovani est Ph. alexandri mais les faibles densités observées de cette espèce ne plaident pas en faveur d’un quelconque rôle. Dans le Dhofar, Ph. sergenti est le principal vecteur prouvé de L. tropica mais Ph. saevus, espèce localement bien plus abondante, constitue une bonne espèce candidate à la transmission.
Keywords: Eco-epidemiology; Leishmania isolation and typing; Oman; Patients; Phlebotomine sandflies.
© J. Rioux et al., published by EDP Sciences, 2020.
Figures




References
-
- Abonnenc E. 1972. Les phlébotomes de la région éthiopienne (Diptera, Psychodidae). Mémoires de l’ORSTOM, 55, 239 p.
-
- Abonnenc E, Rioux JA. 1961. Contribution à l’étude des phlébotomes (Diptera, Psychodidae) du Nord-Tchad, in Mission épidémiologique au Nord-Tchad, Rioux JA, Editor Arts et Métiers Graphiques: Paris: p. 30–53.
-
- Al-Zahrani MA, Peters W, Evans PA, Ching-Chin I, Smith V, Lane RP. 1988. Phlebotomus sergenti, a vector of Leishmania tropica in Saudi Arabia. Transactions of the Royal Society of Tropical Medicine and Hygiene, 82, 416. - PubMed
-
- Al Awaidy S, Al Hashami H. 2020. Zoonotic diseases in Oman: successes, challenges, and future directions. Vector Borne and Zoonotic Diseases, 20(1), 1–9. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
