Super high-pressure balloon versus scoring balloon to prepare severely calcified coronary lesions: the ISAR-CALC randomised trial
- PMID: 33258774
- PMCID: PMC9724952
- DOI: 10.4244/EIJ-D-20-01000
Super high-pressure balloon versus scoring balloon to prepare severely calcified coronary lesions: the ISAR-CALC randomised trial
Abstract
Background: The comparative efficacy of balloon-based techniques to prepare severely calcified coronary lesions before stenting remains poorly studied.
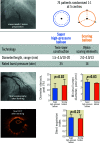
Aims: We sought to compare stent expansion following preparation of severely calcified coronary lesions with either a super high-pressure balloon or a scoring balloon.
Methods: In this randomised, open-label trial, patients with severely calcified coronary lesions were enrolled at five centres in Germany and Switzerland. After unsuccessful lesion preparation with a standard non-compliant balloon (<30% reduction of baseline diameter stenosis), participants were randomised to predilation with either a super high-pressure balloon or a scoring balloon before drug-eluting stent (DES) implantation. The primary endpoint of the study was stent expansion index as assessed by optical coherence tomography (OCT). The key secondary endpoints included angiographic, strategy and procedural success.
Results: OCT data after DES implantation were available for 70 out of 74 patients (94.6%) enrolled. Lesion preparation with a super high-pressure balloon versus a scoring balloon led to a comparable stent expansion index (0.72±0.12 vs 0.68±0.13; p=0.22). Compared with the scoring balloon, the super high-pressure balloon increased the minimum lumen diameter (2.83±0.34 mm vs 2.65±0.36 mm; p=0.03) and reduced the diameter stenosis (11.6±4.8% vs 14.4±5.6%; p=0.02) without difference in terms of angiographic success (100% vs 97.3%; p>0.99). Strategy success (91.9% vs 83.8%; p=0.48) and procedural success (100% vs 89.2%; p=0.12) were numerically more frequent with the super high-pressure balloon versus the scoring balloon.
Conclusions: In patients with severely calcified coronary artery lesions, preparation with a super high-pressure balloon versus a scoring balloon was associated with comparable stent expansion on intravascular imaging and a trend towards improved angiographic performance. Visual summary. A ComparIson of Strategies to PrepAre SeveRely CALCified Coronary Lesions: the ISAR-CALC randomised trial.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Allali reports personal fees from Boston Scientific, outside the submitted work. M. Ayoub reports personal fees from Boston Scientific, outside the submitted work. F. Cuculi reports personal fees from SIS Medical AG, outside the submitted work. M. Bossard reports grants from SIS Medical Switzerland, and personal fees from Abbott Vascular, during the conduct of the study. S. Kufner reports personal fees from AstraZeneca and personal fees from Bristol-Myers Squibb, outside the submitted work. M. Fusaro reports personal fees from SIS Medical AG, outside the submitted work. M. Joner reports personal fees from Biotronik, personal fees from OrbusNeich, grants and personal fees from Boston Scientific, grants and personal fees from Edwards, personal fees from ReCor, personal fees from AstraZeneca, and grants from Amgen, outside the submitted work. R.A. Byrne reports grants to the institution of prior employment from SIS Medical and from Boston Scientific related to the conduct of the study, and grants from CeloNova Biosciences to the institution of prior employment, outside the submitted work. S. Cassese reports personal fees and grants to the institution from SIS Medical AG, outside the submitted work. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures


References
-
- Buiten RA, Ploumen EH, Zocca P, Doggen CJM, van Houwelingen KG, Danse PW, Schotborgh CE, Stoel MG, Scholte M, Linssen GCM, de Man FHAF, von Birgelen C. Three contemporary thin-strut drug-eluting stents implanted in severely calcified coronary lesions of participants in a randomized all-comers trial. Catheter Cardiovasc Interv. 2020;96:E508–15. doi: 10.1002/ccd.28886. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Généreux P, Redfors B, Witzenbichler B, Arsenault MP, Weisz G, Stuckey TD, Rinaldi MJ, Neumann FJ, Metzger DC, Henry TD, Cox DA, Duffy PL, Mazzaferri EL Jr, Francese DP, Marquis-Gravel G, Mintz GS, Kirtane AJ, Maehara A, Mehran R, Stone GW. Two-year outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention of calcified lesions with drug-eluting stents. Int J Cardiol. 2017;231:61–7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.12.150. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Räber L, Mintz GS, Koskinas KC, Johnson TW, Holm NR, Onuma Y, Radu MD, Joner M, Yu B, Jia H, Meneveau N, de la Torre Hernandez JM, Escaned J, Hill J, Prati F, Colombo A, Di Mario C, Regar E, Capodanno D, Wijns W, Byrne RA, Guagliumi G ESC Scientific Document Group. Clinical use of intracoronary imaging. Part 1: guidance and optimization of coronary interventions. An expert consensus document of the European Association of Percutaneous Cardiovascular Interventions. Eur Heart J. 2018;39:3281–300. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

