Regulation of the First Committed Step in Lipopolysaccharide Biosynthesis Catalyzed by LpxC Requires the Essential Protein LapC (YejM) and HslVU Protease
- PMID: 33260377
- PMCID: PMC7730581
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21239088
Regulation of the First Committed Step in Lipopolysaccharide Biosynthesis Catalyzed by LpxC Requires the Essential Protein LapC (YejM) and HslVU Protease
Abstract
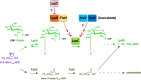
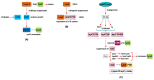
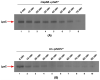
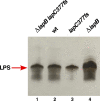
We previously showed that lipopolysaccharide (LPS) assembly requires the essential LapB protein to regulate FtsH-mediated proteolysis of LpxC protein that catalyzes the first committed step in the LPS synthesis. To further understand the essential function of LapB and its role in LpxC turnover, multicopy suppressors of ΔlapB revealed that overproduction of HslV protease subunit prevents its lethality by proteolytic degradation of LpxC, providing the first alternative pathway of LpxC degradation. Isolation and characterization of an extragenic suppressor mutation that prevents lethality of ΔlapB by restoration of normal LPS synthesis identified a frame-shift mutation after 377 aa in the essential gene designated lapC, suggesting LapB and LapC act antagonistically. The same lapC gene was identified during selection for mutations that induce transcription from LPS defects-responsive rpoEP3 promoter, confer sensitivity to LpxC inhibitor CHIR090 and a temperature-sensitive phenotype. Suppressors of lapC mutants that restored growth at elevated temperatures mapped to lapA/lapB, lpxC and ftsH genes. Such suppressor mutations restored normal levels of LPS and prevented proteolysis of LpxC in lapC mutants. Interestingly, a lapC deletion could be constructed in strains either overproducing LpxC or in the absence of LapB, revealing that FtsH, LapB and LapC together regulate LPS synthesis by controlling LpxC amounts.
Keywords: FabZ; HslV/U protease; LapB; LapC; LpxC; RpoE; YejM; lipopolysaccharide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








Similar articles
-
Assembly of lipopolysaccharide in Escherichia coli requires the essential LapB heat shock protein.J Biol Chem. 2014 May 23;289(21):14829-53. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.539494. Epub 2014 Apr 9. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24722986 Free PMC article.
-
An Essential Membrane Protein Modulates the Proteolysis of LpxC to Control Lipopolysaccharide Synthesis in Escherichia coli.mBio. 2020 May 19;11(3):e00939-20. doi: 10.1128/mBio.00939-20. mBio. 2020. PMID: 32430473 Free PMC article.
-
YejM Controls LpxC Levels by Regulating Protease Activity of the FtsH/YciM Complex of Escherichia coli.J Bacteriol. 2020 Aug 25;202(18):e00303-20. doi: 10.1128/JB.00303-20. Print 2020 Aug 25. J Bacteriol. 2020. PMID: 32540932 Free PMC article.
-
Checkpoints That Regulate Balanced Biosynthesis of Lipopolysaccharide and Its Essentiality in Escherichia coli.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 24;23(1):189. doi: 10.3390/ijms23010189. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 35008618 Free PMC article. Review.
-
When, how and why? Regulated proteolysis by the essential FtsH protease in Escherichia coli.Biol Chem. 2017 May 1;398(5-6):625-635. doi: 10.1515/hsz-2016-0302. Biol Chem. 2017. PMID: 28085670 Review.
Cited by
-
A role for the Gram-negative outer membrane in bacterial shape determination.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Feb 4:2023.02.03.527047. doi: 10.1101/2023.02.03.527047. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023 Aug 29;120(35):e2301987120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2301987120. PMID: 36778245 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
(p)ppGpp and moonlighting RNases influence the first step of lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis in Escherichia coli.Microlife. 2023 Jun 20;4:uqad031. doi: 10.1093/femsml/uqad031. eCollection 2023. Microlife. 2023. PMID: 37426605 Free PMC article.
-
Cell Lysis Directed by SulA in Response to DNA Damage in Escherichia coli.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Apr 26;22(9):4535. doi: 10.3390/ijms22094535. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33926096 Free PMC article.
-
Drown Them in Their Own Garbage: a New Strategy To Reverse Polymyxin Resistance?J Bacteriol. 2022 Feb 15;204(2):e0057421. doi: 10.1128/JB.00574-21. Epub 2021 Nov 29. J Bacteriol. 2022. PMID: 34843378 Free PMC article.
-
Signaling through the Salmonella PbgA-LapB regulatory complex activates LpxC proteolysis and limits lipopolysaccharide biogenesis during stationary-phase growth.J Bacteriol. 2024 Apr 18;206(4):e0030823. doi: 10.1128/jb.00308-23. Epub 2024 Mar 27. J Bacteriol. 2024. PMID: 38534107 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Klein G., Lindner B., Brade H., Raina S. Molecular basis of lipopolysaccharide heterogeneity in Escherichia coli: Envelope stress-responsive regulators control the incorporation of glycoforms with a third 3-deoxy-α-D-manno-oct-2-ulosonic acid and rhamnose. J. Biol. Chem. 2011;286:42787–42807. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M111.291799. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

