Quantum Dots: An Emerging Tool for Point-of-Care Testing
- PMID: 33260478
- PMCID: PMC7761335
- DOI: 10.3390/mi11121058
Quantum Dots: An Emerging Tool for Point-of-Care Testing
Abstract
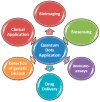
Quantum dots (QDs) are semiconductor crystals in the nanodimension having unique optical and electronic properties that differ from bulk material due to quantum mechanics. The QDs have a narrow emission peak, size-dependent emission wavelength, and broad excitation range which can be utilized for diverse biomedical applications such as molecular imaging, biosensing, and diagnostic systems. This article reviews the current developments of biomedical applications of QDs with special reference to point-of-care testing.
Keywords: microsystem; point-of-care testing; quantum dots.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Michael J. Microsystem Technologies for Medical Applications. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2011;2:355–378. - PubMed
-
- Tai Y.C. Introduction to MEMS. In: Zhou Z., Wang Z., Lin L., editors. Microsystems and Nanotechnology. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2012. pp. 187–206.
-
- Henglein A. Small-particle research physicochemical properties of extremely small colloidal metal and semiconductor particles. Chem. Rev. 1989;89:1861–1873. doi: 10.1021/cr00098a010. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources