Teaghrelin Protects SH-SY5Y Cells against MPP+-Induced Neurotoxicity through Activation of AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α and ERK1/2 Pathways
- PMID: 33260513
- PMCID: PMC7759814
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12123665
Teaghrelin Protects SH-SY5Y Cells against MPP+-Induced Neurotoxicity through Activation of AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α and ERK1/2 Pathways
Abstract
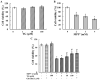
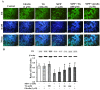
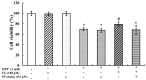
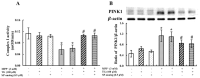
The prevalence and incidence of Parkinson's disease (PD), an age-related neurodegenerative disease, are higher among elderly people. Independent of etiology, dysfunction and loss of dopaminergic neurons are common pathophysiological changes in PD patients with impaired motor and non-motor function. Currently, preventive or therapeutic treatment for combating PD is limited. The ghrelin axis and ghrelin receptor have been implicated in the preservation of dopaminergic neurons and have potential implications in PD treatment. Teaghrelin, a compound originating from Chin-Shin Oolong tea, exhibits ghrelin agonist activity. In this study, the neuroprotective potential of teaghrelin against PD was explored in a cell model in which human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells were treated with the mitochondrial toxin 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium (MPP+). Upon MPP+ exposure, SH-SY5Y cells exhibited decreased mitochondrial complex I activity and apoptotic cell death. Teaghrelin activated AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK)/sirtuin 1(SIRT1)/peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARγ) coactivator-1α (PGC-1α) and extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1 and 2 (ERK1/2) pathways to antagonize MPP+-induced cell death. Herein, we propose that teaghrelin is a potential candidate for the therapeutic treatment of PD.
Keywords: Parkinson’s disease; neurodegeneration; teaghrelin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Teaghrelin protected dopaminergic neurons in MPTP-induced Parkinson's disease animal model by promoting PINK1/Parkin-mediated mitophagy and AMPK/SIRT1/PGC1-α-mediated mitochondrial biogenesis.Environ Toxicol. 2024 Jul;39(7):4022-4034. doi: 10.1002/tox.24275. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Environ Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38622810
-
Overexpression of PGC-1α Influences Mitochondrial Signal Transduction of Dopaminergic Neurons.Mol Neurobiol. 2016 Aug;53(6):3756-3770. doi: 10.1007/s12035-015-9299-7. Epub 2015 Jul 4. Mol Neurobiol. 2016. PMID: 26141122
-
SIRT1 Protects Dopaminergic Neurons in Parkinson's Disease Models via PGC-1α-Mediated Mitochondrial Biogenesis.Neurotox Res. 2021 Oct;39(5):1393-1404. doi: 10.1007/s12640-021-00392-4. Epub 2021 Jul 12. Neurotox Res. 2021. PMID: 34251648
-
SIRT1 mediates salidroside-elicited protective effects against MPP+ -induced apoptosis and oxidative stress in SH-SY5Y cells: involvement in suppressing MAPK pathways.Cell Biol Int. 2018 Jan;42(1):84-94. doi: 10.1002/cbin.10864. Epub 2017 Oct 25. Cell Biol Int. 2018. PMID: 28851138
-
Unveiling the interplay of AMPK/SIRT1/PGC-1α axis in brain health: Promising targets against aging and NDDs.Ageing Res Rev. 2024 Apr;96:102255. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2024.102255. Epub 2024 Mar 14. Ageing Res Rev. 2024. PMID: 38490497 Review.
Cited by
-
Establishment of a Cell Line Stably Expressing the Growth Hormone Secretagogue Receptor to Identify Crocin as a Ghrelin Agonist.Biomolecules. 2022 Dec 5;12(12):1813. doi: 10.3390/biom12121813. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 36551241 Free PMC article.
-
Small Extracellular Vesicles Secreted by Nigrostriatal Astrocytes Rescue Cell Death and Preserve Mitochondrial Function in Parkinson's Disease.Adv Healthc Mater. 2022 Oct;11(20):e2201203. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202201203. Epub 2022 Aug 15. Adv Healthc Mater. 2022. PMID: 35856921 Free PMC article.
-
Empagliflozin repurposing in Parkinson's disease; modulation of oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, AMPK/SIRT-1/PGC-1α, and wnt/β-catenin pathways.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Feb;32(1):777-794. doi: 10.1007/s10787-023-01384-w. Epub 2023 Dec 1. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38038781 Free PMC article.
-
Energy metabolism in health and diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025 Feb 18;10(1):69. doi: 10.1038/s41392-025-02141-x. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2025. PMID: 39966374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Attenuation of Skeletal Muscle Atrophy Induced by Dexamethasone in Rats by Teaghrelin Supplementation.Molecules. 2023 Jan 10;28(2):688. doi: 10.3390/molecules28020688. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36677745 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guan X.M., Yu H., Palyha O.C., McKee K.K., Feighner S.D., Sirinathsinghji D.J., Smith R.G., Van der Ploeg L.H., Howard A.D. Distribution of mRNA encoding the growth hormone secretagogue receptor in brain and peripheral tissues. Brain Res. Mol. Brain Res. 1997;48:23–29. doi: 10.1016/S0169-328X(97)00071-5. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

