Simple and Eco-Friendly Route from Agro-Food Waste to Water Pollutants Removal
- PMID: 33260595
- PMCID: PMC7730895
- DOI: 10.3390/ma13235424
Simple and Eco-Friendly Route from Agro-Food Waste to Water Pollutants Removal
Abstract
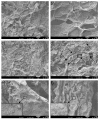
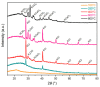
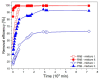
The current study reflects the demand to mitigate the environmental issues caused by the waste from the agriculture and food industry. The crops that do not meet the supply chain requirements and waste from their processing are overfilling landfills. The mentioned wastes contain cellulose, which is the most abundant carbon precursor. Therefore, one of the possibilities of returning such waste into the life cycle could be preparing the activated carbon through an eco-friendly and simple route. Herein, the carrot pulp from the waste was used. Techniques such as thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), elemental analysis (EA), scanning electron microscopy (SEM), Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), Raman spectroscopy, and x-ray diffraction (XRD) were used to investigate the thermal treatment effect during the carbon material preparation. The development of microstructure, phase formation, and chemical composition of prepared material was evaluated. The obtained carbon material was finally tested for water cleaning from a synthetic pollutant such as rhodamine B and phloxine B. An adsorption mechanism was proposed on the base of positron annihilation lifetime spectroscopy (PALS) results and attributed to the responsible interactions. It was shown that a significant carbon sorbent from the organic waste for water purification was obtained.
Keywords: agriculture waste; carbon; carrot pulp; food waste; organic pollutants; sorption; water purification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures








References
-
- Arya M., Lee N., Pellegrino S. Ultralight Structures for Space Solar Power Satellites. [(accessed on 3 September 2020)];2020 Available online: http://www.mananarya.com/docs/2016_sdm_arya.pdf.
-
- Kromoser D.D.B., Preinstorfer D.D.T.P., Kollegger J. Building lightweight structures with carbon-fiber-reinforced polymer--reinforced ultra-high-performance concrete: Research approach, construction materials, and conceptual design of three building components. Struct. Concr. 2019;20:730–744. doi: 10.1002/suco.201700225. - DOI
-
- Elanchezhian C., Ramnath B.V., Ramakrishnan G., Raghavendra K.S., Muralidharan M., Kishore V. Review on metal matrix composites for marine applications. Mater. Today Proc. 2018;5:1211–1218. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2017.11.203. - DOI
-
- Deo R., Starnes J., Holzwarth R. Low-cost composite materials and structures for aircraft applications; Proceedings of the Low Cost Composite Structures and Cost Effective Application of Titanium Alloys in Military Platforms; Loen, Norway. 7–11 May 2001; pp. 1–11.
-
- Maria M. Advanced composite materials of the future in aerospace industry. INCAS Bull. 2013;5:139–150. doi: 10.13111/2066-8201.2013.5.3.14. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

