Towards Climate Resilient and Environmentally Sustainable Health Care Facilities
- PMID: 33260752
- PMCID: PMC7731282
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph17238849
Towards Climate Resilient and Environmentally Sustainable Health Care Facilities
Abstract
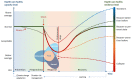
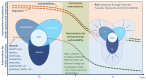
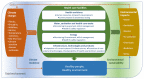
The aim of building climate resilient and environmentally sustainable health care facilities is: (a) to enhance their capacity to protect and improve the health of their target communities in an unstable and changing climate; and (b) to empower them to optimize the use of resources and minimize the release of pollutants and waste into the environment. Such health care facilities contribute to high quality of care and accessibility of services and, by helping reduce facility costs, also ensure better affordability. They are an important component of universal health coverage. Action is needed in at least four areas which are fundamental requirements for providing safe and quality care: having adequate numbers of skilled human resources, with decent working conditions, empowered and informed to respond to these environmental challenges; sustainable and safe management of water, sanitation and health care waste; sustainable energy services; and appropriate infrastructure and technologies, including all the operations that allow for the efficient functioning of a health care facility. Importantly, this work contributes to promoting actions to ensure that health care facilities are constantly and increasingly strengthened and continue to be efficient and responsive to improve health and contribute to reducing inequities and vulnerability within their local settings. To this end, we propose a framework to respond to these challenges.
Keywords: climate change and health; climate resilience; environmental sustainability; health care facilities.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization Operational Framework for Building Climate Resilient Health Systems. [(accessed on 19 October 2020)];2015 Available online: https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/189951/9789241565073_en....
-
- WHO Regional Office for Europe The Tallinn Charter: Health Systems for Health and Wealth. [(accessed on 19 October 2020)];2008 Available online: http://www.euro.who.int/__data/assets/pdf_file/0008/88613/E91438.pdf.
-
- Kruk M.E., Myers M., Varpilah S.T., Dahn B.T. What is a resilient health system? Lessons from Ebola. [(accessed on 19 October 2020)];Lancet. 2015 385:1910–1912. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)60755-3. Available online: https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(15)60755.... - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kutzin J., Sparkes S.P. Health systems strengthening, universal health coverage, health security and resilience. [(accessed on 19 October 2020)];Bull. World Health Organ. 2016 94:2. doi: 10.2471/BLT.15.165050. Available online: https://www.who.int/bulletin/volumes/94/1/15-165050/en/ - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization Environmental Health in Emergencies Health-Care Facilities. [(accessed on 9 October 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/environmental_health_emergencies/services/en/
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical