Polydimethylsiloxane Elastomers Filled with Rod-Like α-MnO2 Nanoparticles: An Interplay of Structure and Electrorheological Performance
- PMID: 33260930
- PMCID: PMC7759881
- DOI: 10.3390/polym12122810
Polydimethylsiloxane Elastomers Filled with Rod-Like α-MnO2 Nanoparticles: An Interplay of Structure and Electrorheological Performance
Abstract
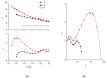
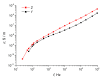
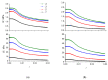
For the first time, electroactive nanocomposite elastomers based on polydimethylsiloxane and filled with rod-like α-MnO2 nanoparticles have been obtained. The curing of the filled elastomer in an electric field, resulting in the ordering of the α-MnO2 particles, had a significant effect on the degree of polymer crosslinking, as well as on the electrorheological characteristics of the nanocomposites obtained through this process, namely the values of the storage and loss moduli. The dielectric spectra of filled elastomers in the frequency range 25-106 Hz were analysed in terms of interfacial relaxation processes. It has been shown, for the first time, that the application of an electric field leads to a decrease in the value of the Payne effect in composite elastomers. Analysis of the rheological effect in the obtained materials has demonstrated the possibility of designing highly efficient electrorheological elastomers that change their elastic properties by 4.3 times in electric fields of up to 2 kV/mm.
Keywords: Payne effect; electrorheological elastomers; manganese dioxide; nanocomposites; smart materials; vulcanisation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Shiga T., Ohta T., Hirose Y., Okada A., Kurauchi T. Electroviscoelastic effect of polymeric composites consisting of polyelectrolyte particles and polymer gel. J. Mater. Sci. 1993;28:1293–1299. doi: 10.1007/BF01191967. - DOI
-
- Shiga T. Deformation and viscoelastic behavior of polymer gels in electric fields. Proc. Jpn. Acad. Ser. B Phys. Biol. Sci. 1998;74:6–11. doi: 10.2183/pjab.74.6. - DOI
-
- Li Y., Li J., Li W., Du H. A state-of-the-art review on magnetorheological elastomer devices. Smart Mater. Struct. 2014;23:123001. doi: 10.1088/0964-1726/23/12/123001. - DOI
-
- Dong X., Niu C., Qi M. Enhancement of electrorheological performance of electrorheological elastomers by improving TiO2 particles/silicon rubber interface. J. Mater. Chem. C. 2016;4:6806–6815. doi: 10.1039/C6TC01447J. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

