The Protective Effects of Flavonoids in Cataract Formation through the Activation of Nrf2 and the Inhibition of MMP-9
- PMID: 33261005
- PMCID: PMC7759919
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12123651
The Protective Effects of Flavonoids in Cataract Formation through the Activation of Nrf2 and the Inhibition of MMP-9
Abstract
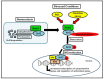
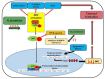
Cataracts account for over half of global blindness. Cataracts formations occur mainly due to aging and to the direct insults of oxidative stress and inflammation to the eye lens. The nuclear factor-erythroid-2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a transcriptional factor for cell cytoprotection, is known as the master regulator of redox homeostasis. Nrf2 regulates nearly 600 genes involved in cellular protection against contributing factors of oxidative stress, including aging, disease, and inflammation. Nrf2 was reported to disrupt the oxidative stress that activates Nuclear factor-κB (NFκB) and proinflammatory cytokines. One of these cytokines is matrix metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9), which participates in the decomposition of lens epithelial cells (LECs) extracellular matrix and has been correlated with cataract development. Thus, during inflammatory processes, MMP production may be attenuated by the Nrf2 pathway or by the Nrf2 inhibition of NFκB pathway activation. Moreover, plant-based polyphenols have garnered attention due to their presumed safety and efficacy, nutritional, and antioxidant effects. Polyphenol compounds can activate Nrf2 and inhibit MMP-9. Therefore, this review focuses on discussing Nrf2's role in oxidative stress and cataract formation, epigenetic effect in Nrf2 activity, and the association between Nrf2 and MMP-9 in cataract development. Moreover, we describe the protective role of flavonoids in cataract formation, targeting Nrf2 activation and MMP-9 synthesis inhibition as potential molecular targets in preventing cataracts.
Keywords: MMP-9; Nrf2; antioxidants; cataracts; flavonoids; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization Blindness, and Vision Impairment Prevention. [(accessed on 6 October 2020)]; Available online: https://www.who.int/blindness/causes/priority/en/index1.html.
-
- Harding J. Biochemistry epidemiology, and pharmacology. Cataract. 1991:195–217.
-
- Babizhayev M.A., Yegorov Y.E. Reactive Oxygen Species, and the Aging Eye: Specific Role of Metabolically Active Mitochondria in Maintaining Lens Function and in the Initiation of the Oxidation-Induced Maturity Onset Cataract—A Novel Platform of Mitochondria-Targeted Antioxidants with Broad Therapeutic Potential for Redox Regulation and Detoxification of Oxidants in Eye Diseases. Am. J. Ther. 2016;23:e98–e117. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0b013e3181ea31ff. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

