Serum-Derived Exosomal MicroRNA Profiles Can Predict Poor Survival Outcomes in Patients with Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma
- PMID: 33261029
- PMCID: PMC7761501
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers12123548
Serum-Derived Exosomal MicroRNA Profiles Can Predict Poor Survival Outcomes in Patients with Extranodal Natural Killer/T-Cell Lymphoma
Abstract
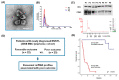
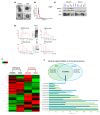
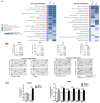
Exosomes containing microRNAs (miRNAs) might have utility as biomarkers to predict the risk of treatment failure in extranodal NK/T-cell lymphoma (ENKTL) because exosomal cargo miRNAs could reflect tumor aggressiveness. We analyzed the exosomal miRNAs of patients in favorable (n = 22) and poor outcome (n = 23) groups in a training cohort. Then, using the Nanostring nCounter® microRNA array, we compared them with miRNAs identified in human NK/T lymphoma (NKTL) cell line-derived exosomes to develop exosomal miRNA profiles. We validated the prognostic value of serum exosomal miRNA profiles with an independent cohort (n = 85) and analyzed their association with treatment resistance using etoposide-resistant cell lines. A comparison of the top 20 upregulated miRNAs in the training cohort with poor outcomes with 16 miRNAs that were upregulated in both NKTL cell lines, identified five candidate miRNAs (miR-320e, miR-4454, miR-222-3p, miR-21-5p, and miR-25-3p). Among these, increased levels of exosomal miR-4454, miR-21-5p, and miR-320e were associated with poor overall survival in the validation cohort. Increased levels were also found in relapsed patients post-treatment. These three miRNAs were overexpressed in NKTL cell lines that were resistant to etoposide. Furthermore, transfection of NKTL cell lines with miR-21-5p and miR-320e induced an increase in expression of the proinflammatory cytokines such as macrophage inflammatory protein 1 alpha. These studies show that serum levels of exosomal miR-21-5p, miR-320e, and miR-4454 are increased in ENKTL patients with poor prognosis. Upregulation of these exosomal miRNAs in treatment-resistant cell lines suggests they have a role as biomarkers for the identification of ENKTL patients at high risk of treatment failure.
Keywords: NK/T-cell lymphoma; biomarker; exosome; microRNA cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Théry C., Witwer K.W., Aikawa E., Alcaraz M.J., Anderson J.D., Andriantsitohaina R., Antoniou A., Arab T., Archer F., Atkin-Smith G.K., et al. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles 2018 (MISEV2018): A position statement of the International Society for Extracellular Vesicles and update of the MISEV2014 guidelines. J. Extracell. Vesicles. 2018;7:1535750. doi: 10.1080/20013078.2018.1535750. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

