Application of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) in Phage Displayed Peptide Selection to Support the Identification of Arsenic-Binding Motifs
- PMID: 33261041
- PMCID: PMC7759992
- DOI: 10.3390/v12121360
Application of Next Generation Sequencing (NGS) in Phage Displayed Peptide Selection to Support the Identification of Arsenic-Binding Motifs
Abstract
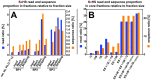
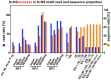
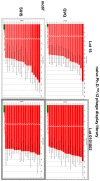
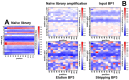
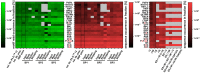
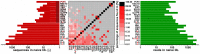
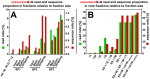
Next generation sequencing (NGS) in combination with phage surface display (PSD) are powerful tools in the newly equipped molecular biology toolbox for the identification of specific target binding biomolecules. Application of PSD led to the discovery of manifold ligands in clinical and material research. However, limitations of traditional phage display hinder the identification process. Growth-based library biases and target-unrelated peptides often result in the dominance of parasitic sequences and the collapse of library diversity. This study describes the effective enrichment of specific peptide motifs potentially binding to arsenic as proof-of-concept using the combination of PSD and NGS. Arsenic is an environmental toxin, which is applied in various semiconductors as gallium arsenide and selective recovery of this element is crucial for recycling and remediation. The development of biomolecules as specific arsenic-binding sorbents is a new approach for its recovery. Usage of NGS for all biopanning fractions allowed for evaluation of motif enrichment, in-depth insight into the selection process and the discrimination of biopanning artefacts, e.g., the amplification-induced library-wide reduction in hydrophobic amino acid proportion. Application of bioinformatics tools led to the identification of an SxHS and a carboxy-terminal QxQ motif, which are potentially involved in the binding of arsenic. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first report of PSD combined with NGS of all relevant biopanning fractions.
Keywords: Illumina; NGS; arsenic; biopanning; interaction; motif; oxyanion; peptide; phage display; target-unrelated peptide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Cullen W.R. Is Arsenic An Aphrodisiac? Royal Society of Chemistry; Cambridge, UK: 2008. - DOI
-
- Ahuja S., editor. Arsenic Contamination of Groundwater. John Wiley & Sons, Inc.; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2008. - DOI
-
- States J.C., editor. Arsenic: Exposure Sources, Health Risks and Mechanisms of Toxicity. John Wiley & Sons, Inc; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2015. - DOI
-
- Yamauchi H., Takata A., Cao Y., Nakamura K. The Development and Purposes of Arsenic Detoxification Technology. Springer; Singapore: 2019. pp. 199–211. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

