Solubility and Thermal Degradation of Quercetin in CO2-Expanded Liquids
- PMID: 33261120
- PMCID: PMC7730818
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules25235582
Solubility and Thermal Degradation of Quercetin in CO2-Expanded Liquids
Abstract
The solubility of quercetin and its thermal degradation was studied in CO2-expanded ethanol and ethyl lactate. An equipment setup was constructed that enabled the separation of the products of degradation while quantifying the solubility of quercetin. Three different conditions of temperature were analyzed (308, 323, and 343 K) at 10 MPa. Higher solubility and thermal degradation of quercetin were observed for CO2-expanded ethyl lactate in comparison with CO2-expanded ethanol. At the same time, as the amount of CO2 was increased in the CO2-expanded liquids mixtures, the thermal degradation of quercetin decreased for almost all the conditions of temperature considered in this work. The importance of considering thermal degradation while performing solubility measurements of compounds that are thermally unstable such as quercetin was highlighted.
Keywords: gas-expanded liquid; green solvent; quercetin; solubility; subcritical fluid; thermal degradation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
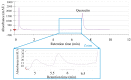
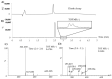

References
-
- Ben Yakoub A.R., Abdehedi O., Jridi M., Elfalleh W., Nasri M., Ferchichi A. Flavonoids, phenols, antioxidant, and antimicrobial activities in various extracts from Tossa jute leave (Corchorus olitorus L.) Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018;118:206–213. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2018.03.047. - DOI
-
- Vetrova E.V., Maksimenko E.V., Borisenko S.N., Lekar A.V., Borisenko N.I., Minkin V.I. Extraction of Rutin and Quercetin Antioxidants from the Buds of Sophora Japonica (Sophora japonica L.) by Subcritical Water. Russ. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2017;11:1202–1206. doi: 10.1134/S1990793117070193. - DOI
-
- Lichtenthaler R.N. Gerd Brunner: Gas Extraction—An Introduction to Fundamentals of Supercritical Fluids and the Application to Separation Processes. Topics in Physical Chemistry, Vol. 4, eds. H. Baumgärtel, E. U. Franck, W. Grünbein. Steinkopff, Darmstadt/Springer, New York, 1994, 387 S., DM 64,—. Berichte Bunsenges. Phys. Chem. 1996;100:1090–1091.
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

