Effect of masks on speech intelligibility in auralized classrooms
- PMID: 33261397
- PMCID: PMC7857496
- DOI: 10.1121/10.0002450
Effect of masks on speech intelligibility in auralized classrooms
Abstract
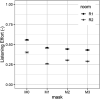
This study explored the effects of wearing face masks on classroom communication. The effects of three different types of face masks (fabric, surgical, and N95 masks) on speech intelligibility (SI) presented to college students in auralized classrooms were evaluated. To simulate realistic classroom conditions, speech stimuli were presented in the presence of speech-shaped noise with a signal-to-noise ratio of +3 dB under two different reverberation times (0.4 s and 3.1 s). The use of fabric masks yielded a significantly greater reduction in SI compared to the other masks. Therefore, surgical masks or N95 masks are recommended in teaching environments.
Figures



References
-
- Steeneken H. J. and Houtgast T., “ Mutual dependence of the octave-band weights in predicting speech intelligibility,” Speech Commun. 28(2), 109–123 (1999). 10.1016/S0167-6393(99)00007-2 - DOI
-
- Goldin A., Weinstein B. E., and Shiman N., “ How do medical masks degrade speech perception?,” Hear. Rev. 27(5), 8–9 (2020).
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

