Copy number gain of pro-inflammatory genes in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure
- PMID: 33261607
- PMCID: PMC7709420
- DOI: 10.1186/s12920-020-00835-5
Copy number gain of pro-inflammatory genes in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure
Abstract
Background: Host genetic factors such as single nucleotide variations may play a crucial role in the onset and progression of HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure (ACLF). However, the underlying genomic copy number variations (CNVs) involved in the pathology are currently unclear.
Methods: We genotyped two cohorts with 389 HBV-related ACLF patients and 391 asymptomatic HBV carriers (AsCs), and then carried out CNV-based global burden analysis and a genome-wide association study (GWAS).
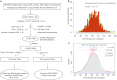
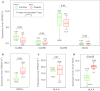
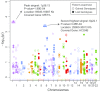
Results: For 1874 rare CNVs, HBV-related ACLF patients exhibited a high burden of deletion segments with a size of 100-200 kb (P value = 0.04), and the related genes were significantly enriched in leukocyte transendothelial migration pathway (P value = 4.68 × 10-3). For 352 common CNVs, GWAS predicted 17 significant association signals, and the peak one was a duplication segment located on 1p36.13 (~ 38 Kb, P value = 1.99 × 10-4, OR = 2.66). The associated CNVs resulted in more copy number of pro-inflammatory genes (MST1L, DEFB, and HCG4B) in HBV-related ACLF patients than in AsC controls.
Conclusions: Our results suggested that the impact of host CNV on HBV-related ACLF may be through decreasing natural immunity and enhancing host inflammatory response during HBV infection. The findings highlighted the potential importance of gene dosage on excessive hepatic inflammation of this disease.
Keywords: Acute-on-chronic liver failure; Copy number variations; GWAS; HBV-ACLF; HBV-related ACLF.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide association study identifies HLA-DR variants conferring risk of HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure.Gut. 2018 Apr;67(4):757-766. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2016-313035. Epub 2017 Jan 27. Gut. 2018. PMID: 28130311
-
[Correlation between interleukin-6 single nucleotide polymorphism and the occurrence and prognosis of hepatitis B virus-associated acute-on-chronic liver failure].Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2019 Apr 20;27(4):250-255. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.1007-3418.2019.04.003. Zhonghua Gan Zang Bing Za Zhi. 2019. PMID: 31082334 Chinese.
-
RNA Profiling Analysis of the Serum Exosomes Derived from Patients with Chronic Hepatitis and Acute-on-chronic Liver Failure Caused By HBV.Sci Rep. 2020 Jan 30;10(1):1528. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-58233-x. Sci Rep. 2020. PMID: 32001731 Free PMC article.
-
The fibrogenic process and the unleashing of acute-on-chronic liver failure.Clin Mol Hepatol. 2020 Jan;26(1):7-15. doi: 10.3350/cmh.2019.0011. Epub 2019 Jun 14. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2020. PMID: 31195778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Host genetic factors affecting hepatitis B infection outcomes: Insights from genome-wide association studies.World J Gastroenterol. 2018 Aug 14;24(30):3347-3360. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v24.i30.3347. World J Gastroenterol. 2018. PMID: 30122875 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Fully exploiting SNP arrays: a systematic review on the tools to extract underlying genomic structure.Brief Bioinform. 2022 Mar 10;23(2):bbac043. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac043. Brief Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 35211719 Free PMC article.
-
A Lower HCC Incidence in Chronic HBV-Infected Patients Recovered from Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure: A Prospective Cohort Study.J Oncol. 2022 Oct 27;2022:5873002. doi: 10.1155/2022/5873002. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36339647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Moreau R, Jalan R, Gines P, Pavesi M, Angeli P, Cordoba J, Durand F, Gustot T, Saliba F, Domenicali M, et al. Acute-on-chronic liver failure is a distinct syndrome that develops in patients with acute decompensation of cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 2013;144(7):1426–U1189. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2013.02.042. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bernsmeier C, Pop OT, Singanayagam A, Triantafyllou E, Patel VC, Weston CJ, Curbishley S, Sadiq F, Vergis N, Khamri W, et al. Patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure have increased numbers of regulatory immune cells expressing the receptor tyrosine kinase MERTK. Gastroenterology. 2015;148(3):603. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.11.045. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

