Incidence and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C in China and the United States
- PMID: 33262356
- PMCID: PMC7708980
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-77515-y
Incidence and risk factors of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with hepatitis C in China and the United States
Abstract
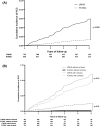
Hepatitis C virus (HCV) infection is the main cause of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) in the United States (US) and an increasingly common cause of HCC in China. We aimed to evaluate the incidence and risk factors of HCC in HCV patients in the US and China. 795 HCV RNA + patients without HCC from University of Michigan Health System (UMHS) in the US and 854 from Peking University Health Sciences Center (PUHSC) in China were prospectively followed for a median of 3.2 and 4.0 years, respectively. 45.4% UMHS and 16.2% PUHSC patients had cirrhosis. 57.6% UMHS and 52.0% PUHSC patients achieved SVR. 45 UMHS and 13 PUHSC patients developed HCC. Cumulative incidence of HCC at 5 years was 7.6% in UMHS and 1.8% in PUHSC cohort (P < 0.001). Ten patients not diagnosed with cirrhosis at enrollment but median APRI ≥ 2.0 developed HCC. Multivariate analysis showed age, gender, cirrhosis and APRI were predictors of HCC while study site and SVR were not. In this study of HCV patients, HCC incidence in the PUHSC cohort was lower than in the UMHS cohort, due to lower proportion of PUHSC patients with cirrhosis. APRI can identify risk of HCC among patients not diagnosed to have cirrhosis.
Conflict of interest statement
Anna S. Lok has received research grants from Bristol-Myers Squibb, TARGET PharmaSolutions, and Gilead, and has served as an advisor for Gilead and TARGET PharmaSolutions. Lai Wei has received research grants from Roche and Bristol-Myers Squibb, and has served as an advisor for Gilead and Abbott. Neehar D. Parikh has received research grants from Bayer, Exact Sciences, and Target PharmaSolutions, and he has served as a consultant for Bayer, Exelixis, Eli Lilly, Eisai, and Bristol Myers-Squibb. Other authors have no conflict of interests to disclose.
Figures

References
-
- World Health Organization. Hepatitis C. Available at: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hepatitis-c. Updated July 2020.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

