Transfer learning with chest X-rays for ER patient classification
- PMID: 33262425
- PMCID: PMC7708466
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-020-78060-4
Transfer learning with chest X-rays for ER patient classification
Abstract
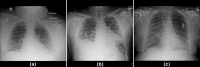
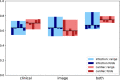
One of the challenges with urgent evaluation of patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) in the emergency room (ER) is distinguishing between cardiac vs infectious etiologies for their pulmonary findings. We conducted a retrospective study with the collected data of 171 ER patients. ER patient classification for cardiac and infection causes was evaluated with clinical data and chest X-ray image data. We show that a deep-learning model trained with an external image data set can be used to extract image features and improve the classification accuracy of a data set that does not contain enough image data to train a deep-learning model. An analysis of clinical feature importance was performed to identify the most important clinical features for ER patient classification. The current model is publicly available with an interface at the web link: http://nbttranslationalresearch.org/ .
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmed, A. & Graber, M. A. Evaluation of the Adult with Dyspnea in the Emergency Department (ed. Jonathan Grayzel, F.) (2020).
-
- Holubar, M. & Deresinski, S. Antimicrobial Stewardship in Hospital Settings (ed. Sheila Bond, M.) (2020).
-
- Rajpurkar, P. et al. CheXNet: radiologist-level pneumonia detection on chest X-rays with deep learning. arXiv.:1711.05225 (2017).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

