Antiviral Effects of Oleandrin
- PMID: 33262663
- PMCID: PMC7686471
- DOI: 10.2147/JEP.S273120
Antiviral Effects of Oleandrin
Abstract
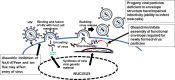
Over the past 15 years, investigators have reported on the utility and safety of cardiac glycosides for numerous health benefits including those as treatments for malignant disease, stroke-mediated ischemic injury and certain neurodegenerative diseases. In addition to those, there is a growing body of evidence for novel antiviral effects of selected cardiac glycoside molecules. One unique cardiac glycoside, oleandrin derived from Nerium oleander, has been reported to have antiviral activity specifically against 'enveloped' viruses including HIV and HTLV-1. Importantly, a recent publication has presented in vitro evidence for oleandrin's ability to inhibit production of infectious virus particles when used for treatment prior to, as well as after infection by SARS-CoV-2/COVID-19. This review will highlight the known in vitro antiviral effects of oleandrin as well as present previously unpublished effects of this novel cardiac glycoside against Ebola virus, Cytomegalovirus, and Herpes simplex viruses.
Keywords: K-ATPase; Na; Nerium oleander; antiviral therapy; oleandrin; virus.
© 2020 Newman et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Robert A. Newman is the Chief Science Officer and a Director of Phoenix Biotechnology, Inc., reports personal fees from Phoenix Biotechnology, Inc., during the conduct of the study, and has a patent issued: 10,729,735. K Jagannadha Sastry reports personal fees from Phoenix Biotechnology Inc., during the conduct of the study and outside the submitted work. Ravit Arav-Boger reports grants from Nerium Biotechnology, during the conduct of the study and has a patent, Inhibition of Human Cytomegalovirus Replication by Novel Digitoxin Analogs Depends on Specific Alpha Isoforms of the Na-K-ATPase Pump, issued to US patent application US20160143934. Rick Matos is a Director and consultant for Phoenix Biotechnology. Robert Harrod reports personal fees from Phoenix Biotechnology, Inc., outside the submitted work. The other authors report no other potential conflicts of interest for this work.
Figures

References
-
- Schoner W, Scheiner-Bobis G. Endogenous and exogenous cardiac glycosides and their mechanisms of action. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 2007;7(3):173–189. - PubMed
-
- Botelho AFM, Pierezan F, Soto-Blanco B, Melo MM. A review of cardiac glycosides: structure, toxicokinetics, clinical signs, diagnosis and antineoplastic potential. Toxicon. 2019;158:63–68. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

