Ras Pathways on Prox1 and Lymphangiogenesis: Insights for Therapeutics
- PMID: 33263009
- PMCID: PMC7688453
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.597374
Ras Pathways on Prox1 and Lymphangiogenesis: Insights for Therapeutics
Abstract
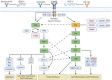
Over the past couple of decades, lymphatics research has accelerated and gained a much-needed recognition in pathophysiology. As the lymphatic system plays heavy roles in interstitial fluid drainage, immune surveillance and lipid absorption, the ablation or excessive growth of this vasculature could be associated with many complications, from lymphedema to metastasis. Despite their growing importance in cancer, few anti-lymphangiogenic therapies exist today, as they have yet to pass phase 3 clinical trials and acquire FDA approval. As such, many studies are being done to better define the signaling pathways that govern lymphangiogenesis, in hopes of developing new therapeutic approaches to inhibit or stimulate this process. This review will cover our current understanding of the Ras signaling pathways and their interactions with Prox1, the master transcriptional switch involved in specifying lymphatic endothelial cell fate and lymphangiogenesis, in hopes of providing insights to lymphangiogenesis-based therapies.
Keywords: ERK pathway; PI3K-AKT pathway; Prox1; Ras; lymphangiogenesis; lymphatics.
Copyright © 2020 Bui and Hong.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Potential lymphangiogenesis therapies: Learning from current antiangiogenesis therapies-A review.Med Res Rev. 2018 Sep;38(6):1769-1798. doi: 10.1002/med.21496. Epub 2018 Mar 12. Med Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29528507 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Prox1 is a master control gene in the program specifying lymphatic endothelial cell fate.Dev Dyn. 2002 Nov;225(3):351-7. doi: 10.1002/dvdy.10163. Dev Dyn. 2002. PMID: 12412020
-
Lymphatic fate specification: an ERK-controlled transcriptional program.Microvasc Res. 2014 Nov;96:10-5. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2014.07.016. Epub 2014 Aug 15. Microvasc Res. 2014. PMID: 25132472 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fluorescent reporter transgenic mice for in vivo live imaging of angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis.Angiogenesis. 2018 Nov;21(4):677-698. doi: 10.1007/s10456-018-9629-2. Epub 2018 Jul 3. Angiogenesis. 2018. PMID: 29971641 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The lymphatic vasculature revisited-new developments in the zebrafish.Methods Cell Biol. 2017;138:221-238. doi: 10.1016/bs.mcb.2016.11.001. Epub 2016 Dec 29. Methods Cell Biol. 2017. PMID: 28129845 Review.
Cited by
-
Low Efficacy of Genetic Tests for the Diagnosis of Primary Lymphedema Prompts Novel Insights into the Underlying Molecular Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jul 3;23(13):7414. doi: 10.3390/ijms23137414. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35806420 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk Between microRNAs and the Pathological Features of Secondary Lymphedema.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021 Oct 18;9:732415. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2021.732415. eCollection 2021. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2021. PMID: 34733847 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeted Therapy for Complex Lymphatic Anomalies in Patients with Noonan Syndrome and Related Disorders.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Jun 26;26(13):6126. doi: 10.3390/ijms26136126. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40649904 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in lymphatic metastasis of non-small cell lung cancer.Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Apr 2;22(1):201. doi: 10.1186/s12964-024-01574-1. Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 38566083 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lymphatic endothelial sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor 1 enhances macrophage clearance via lymphatic system following myocardial infarction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 8;9:872102. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.872102. eCollection 2022. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 36003911 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

