Analysis of the immune response to sciatic nerve injury identifies efferocytosis as a key mechanism of nerve debridement
- PMID: 33263277
- PMCID: PMC7735761
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.60223
Analysis of the immune response to sciatic nerve injury identifies efferocytosis as a key mechanism of nerve debridement
Abstract
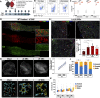
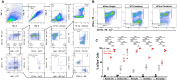
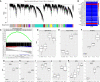
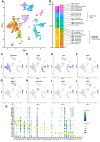
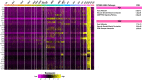
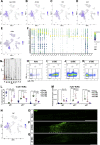
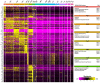
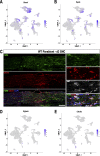
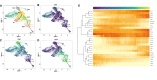
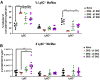
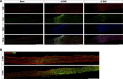
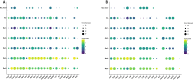
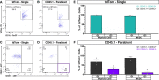
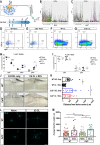
Sciatic nerve crush injury triggers sterile inflammation within the distal nerve and axotomized dorsal root ganglia (DRGs). Granulocytes and pro-inflammatory Ly6Chigh monocytes infiltrate the nerve first and rapidly give way to Ly6Cnegative inflammation-resolving macrophages. In axotomized DRGs, few hematogenous leukocytes are detected and resident macrophages acquire a ramified morphology. Single-cell RNA-sequencing of injured sciatic nerve identifies five macrophage subpopulations, repair Schwann cells, and mesenchymal precursor cells. Macrophages at the nerve crush site are molecularly distinct from macrophages associated with Wallerian degeneration. In the injured nerve, macrophages 'eat' apoptotic leukocytes, a process called efferocytosis, and thereby promote an anti-inflammatory milieu. Myeloid cells in the injured nerve, but not axotomized DRGs, strongly express receptors for the cytokine GM-CSF. In GM-CSF-deficient (Csf2-/-) mice, inflammation resolution is delayed and conditioning-lesion-induced regeneration of DRG neuron central axons is abolished. Thus, carefully orchestrated inflammation resolution in the nerve is required for conditioning-lesion-induced neurorepair.
Keywords: axon regeneration; conditioning lesion; dorsal root ganglia; efferocytosis; mouse; neuroscience; scRNA sequencing; sciatic nerve injury.
© 2020, Kalinski et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AK, CY, LH, PD, RK, RP, HH, CJ, RK, KC, JJ, EH, DG, BS, RG No competing interests declared
Figures

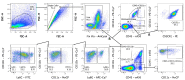
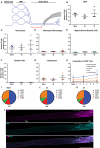
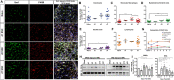
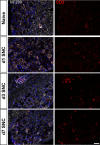






References
-
- Arthur-Farraj PJ, Latouche M, Wilton DK, Quintes S, Chabrol E, Banerjee A, Woodhoo A, Jenkins B, Rahman M, Turmaine M, Wicher GK, Mitter R, Greensmith L, Behrens A, Raivich G, Mirsky R, Jessen KR. c-Jun reprograms schwann cells of injured nerves to generate a repair cell essential for regeneration. Neuron. 2012;75:633–647. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2012.06.021. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

