Reperfused hemorrhagic myocardial infarction in rats
- PMID: 33264359
- PMCID: PMC7710030
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0243207
Reperfused hemorrhagic myocardial infarction in rats
Abstract
Background: Intramyocardial hemorrhage following reperfusion is strongly associated with major adverse cardiovascular events in myocardial infarction (MI) patients; yet the mechanisms contributing to these outcomes are not well understood. Large animal models have been used to investigate intramyocardial hemorrhage, but they are exorbitantly expensive and difficult to use for mechanistic studies. In contrast, rat models are widely used to investigate mechanistic aspects of cardiovascular physiology, but a rat model that consistently recapitulates the characteristics of an hemorrhagic MI does not exist. To bridge this gap, we investigated the physiological conditions of MI that would create intramyocardial hemorrhage in rats so that a reliable model of hemorrhagic MI would become available for basic research.
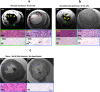
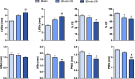
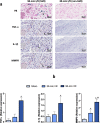
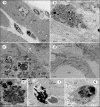
Methods & results: Sprague-Dawley rats underwent either a 90-minute (90-min) ischemia and then reperfusion (I/R) (n = 22) or 30-minute (30-min) I/R (n = 18) of the left anterior descending coronary artery. Sham rats (n = 12) were used as controls. 90-min I/R consistently yielded hemorrhagic MI, while 30-min I/R consistently yielded non-hemorrhagic MI. Twenty-four hours post-reperfusion, ex-vivo late-gadolinium-enhancement (LGE) and T2* cardiac MRI performed on excised hearts from 90-min I/R rats revealed colocalization of iron deposits within the scarred tissue; however, in 30-min I/R rats scar was evident on LGE but no evidence of iron was found on T2* CMR. Histological studies verified tissue damage (H&E) detected on LGE and the presence of iron (Perl's stain) observed on T2*-CMR. At week 4 post-reperfusion, gene and protein expression of proinflammatory markers (TNF-α, IL-1β and MMP-9) were increased in the 90-min I/R group when compared to 30-min I/R groups. Further, transmission electron microscopy performed on 90-min I/R myocardium that were positive for iron on T2* CMR and Perl's stain showed accumulation of granular iron particles within the phagosomes.
Conclusion: Ischemic time prior to reperfusion is a critical factor in determining whether a MI is hemorrhagic or non-hemorrhagic in rats. Specifically, a period of 90-min of ischemia prior to reperfusion can produce rat models of hemorrhagic MI, while 30-minutes of ischemia prior to reperfusion can ensure that the MIs are non-hemorrhagic. Hemorrhagic MIs in rats result in marked increase in iron deposition, proinflammatory burden and adverse left-ventricular remodeling compared to rats with non-hemorrhagic MIs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Ir Degano, Subirana I, Fusco D, Tavazzi L, Kirchberger I, Farmakis D, et al. Percutaneous Coronary Intervention Reduces Mortality In Myocardial Infarction Patients With Comorbidities: Implications For Elderly Patients With Diabetes Or Kidney Disease. Int J Cardiol. 2017;249:83–9. 10.1016/j.ijcard.2017.07.054 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

