Patterns of healthcare resource utilization in patients with sarcoidosis: a cross-sectional study
- PMID: 33264377
- PMCID: PMC7690057
- DOI: 10.36141/svdld.v37i3.9261
Patterns of healthcare resource utilization in patients with sarcoidosis: a cross-sectional study
Abstract
Background: Limited data are available on healthcare resource use and costs in patients with sarcoidosis.
Objectives: The primary aim of this study was to describe cost-drivers of the top 1% and top ≥1-5% high-cost patients with sarcoidosis. The secondary aim was to compare costs of patients with and without fatigue complaints and to compare comorbidities.
Methods: We conducted a retrospective observational cross-sectional study in 200 patients diagnosed with sarcoidosis. Hospital administrative databases were used to extract healthcare utilization on the individual patient level. Healthcare costs were categorized into nine groups.
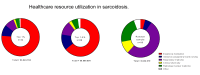
Results: Average total health care costs for the top 1% (n=22), top ≥1%-5% (n=88) and bottom 95% beneficiaries (n=90) were € 108.296, €53.237 and €4.817, respectively. Mean treatment time in days for the top 1%, top ≥1-5% and the random sample of the bottom 95% was 1688 days (±225), 1412 days (±367) and 775 days (±659), respectively. Mean annual costs for the top 1%, top ≥1-5% and the random sample of the bottom 95% are €51.082, €27.840 and €8.692, respectively. We identified three cost-drivers in the top 5% high-cost patients: 1) expensive medication, 2) intensive care and 3) costs made at the respiratory unit. Patients with and without fatigue showed to have comparable mean costs. High-cost patients were more likely to have multiple organs involved due to sarcoidosis.
Conclusions: We identified expensive medication as the main cost-driver in the top 5% high-cost patients with sarcoidosis. The study findings can help to tailor interventions for improving the quality of care and reducing overall costs. (Sarcoidosis Vasc Diffuse Lung Dis 2020; 37 (3): e2020002).
Keywords: costs; quality of care; sarcoidosis.
Copyright: © 2020 SARCOIDOSIS VASCULITIS AND DIFFUSE LUNG DISEASES.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Drivers of Healthcare Costs Among the Costliest Patients With Psoriasis Over Three Years in a United States Health Plan.J Drugs Dermatol. 2017 Jul 1;16(7):651-658. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017. PMID: 28697216
-
Economic burden of sarcoidosis in a commercially-insured population in the United States.J Med Econ. 2017 Oct;20(10):1048-1055. doi: 10.1080/13696998.2017.1351371. Epub 2017 Jul 21. J Med Econ. 2017. PMID: 28678623
-
[Characteristics and healthcare utilization of patients with highest costs of care].Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2017;161:D2220. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd. 2017. PMID: 29219799 Dutch.
-
Critical care nursing service costs: Comparison of the top-down versus bottom-up micro-costing approach in Brazil.J Nurs Manag. 2021 Sep;29(6):1778-1784. doi: 10.1111/jonm.13313. Epub 2021 Apr 9. J Nurs Manag. 2021. PMID: 33772914
-
Economic burden of bilateral neovascular age-related macular degeneration: multi-country observational study.Pharmacoeconomics. 2008;26(1):57-73. doi: 10.2165/00019053-200826010-00006. Pharmacoeconomics. 2008. PMID: 18088159
References
-
- Baughman RP, Lower EE, Gibson K. Pulmonary manifestations of sarcoidosis. Presse Med. Elsevier. 2012;41:e289–e302. - PubMed
-
- Drent M, Lower EE, De Vries J. Sarcoidosis-associated fatigue. Eur. Respir. 2012;40:255–263. - PubMed
-
- Costabel U, Hunninghake GW, Committee SS. ATS/ERS/WASOG statement on sarcoidosis. Eur. Respir. J. Wiley Online Library. 1999;14:735–737. - PubMed
-
- Iannuzzi MC, Fontana JR. Sarcoidosis: clinical presentation, immunopathogenesis, and therapeutics. Jama American Medical Association. 2011;305:391–399. - PubMed
-
- De Vries J, Drent M. Semin. Respir. Crit. Care Med. New York: Thieme Medical Publishers; c1994-; 2007. Quality of life and health status in sarcoidosis: a review; pp. 121–127. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources