Continuous focus on COVID-19 epidemic: Changes in China's clinical guidance
- PMID: 33264484
- PMCID: PMC7744829
- DOI: 10.1111/ijcp.13869
Continuous focus on COVID-19 epidemic: Changes in China's clinical guidance
Abstract
Backgrounds: The epidemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading across the world. As the first country who suffered from the outbreak, China has been taking strict and effective measures to contain the epidemic and treat the disease under the instruction of updating guidance.
Aims: To compare the changes and updates in China's clinical guidance for COVID-19.
Methods: We explored China's experience in dealing with the epidemic by longitudinal comparison of China's clinical guidance for COVID-19.
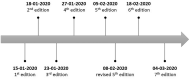
Results: As of March 4, there are 7 editions of the guidance. With the increasing understanding of COVID-19, changes have been made in aetiology, epidemiology, pathology, clinical features, diagnostic criteria, clinical classification, and treatment.
Conclusions: We have made a summary of the changes and updates in China's clinical guidance for COVID-19, which mirrors the deepening understanding of the disease over the course of fighting it, hoping to help clinicians worldwide.
© 2020 John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials