Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers from UVB exposure induce a hypermetabolic state in keratinocytes via mitochondrial oxidative stress
- PMID: 33264701
- PMCID: PMC7708942
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2020.101808
Cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers from UVB exposure induce a hypermetabolic state in keratinocytes via mitochondrial oxidative stress
Abstract
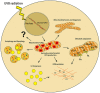
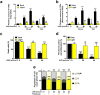
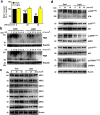
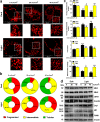
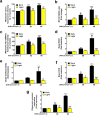
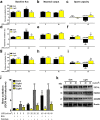
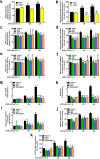
Ultraviolet B radiation (UVB) is an environmental complete carcinogen, which induces and promotes keratinocyte carcinomas, the most common human malignancies. UVB induces the formation of cyclobutane pyrimidine dimers (CPDs). Repairing CPDs through nucleotide excision repair is slow and error-prone in placental mammals. In addition to the mutagenic and malignancy-inducing effects, UVB also elicits poorly understood complex metabolic changes in keratinocytes, possibly through CPDs. To determine the effects of CPDs, CPD-photolyase was overexpressed in keratinocytes using an N1-methyl pseudouridine-containing in vitro-transcribed mRNA. CPD-photolyase, which is normally not present in placental mammals, can efficiently and rapidly repair CPDs to block signaling pathways elicited by CPDs. Keratinocytes surviving UVB irradiation turn hypermetabolic. We show that CPD-evoked mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production, followed by the activation of several energy sensor enzymes, including sirtuins, AMPK, mTORC1, mTORC2, p53, and ATM, is responsible for the compensatory metabolic adaptations in keratinocytes surviving UVB irradiation. Compensatory metabolic changes consist of enhanced glycolytic flux, Szent-Györgyi-Krebs cycle, and terminal oxidation. Furthermore, mitochondrial fusion, mitochondrial biogenesis, and lipophagy characterize compensatory hypermetabolism in UVB-exposed keratinocytes. These properties not only support the survival of keratinocytes, but also contribute to UVB-induced differentiation of keratinocytes. Our results indicate that CPD-dependent signaling acutely maintains skin integrity by supporting cellular energy metabolism.
Keywords: CPD; Keratinocyte; Mitochondria; Photolyase mRNA; UVB.
Copyright © 2020 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
G.P. is a consultant for ADC Therapeutics and Buffalo Biolabs. Other authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

