Adaptive Synchronization of Fractional-Order Complex-Valued Neural Networks with Discrete and Distributed Delays
- PMID: 33265215
- PMCID: PMC7512617
- DOI: 10.3390/e20020124
Adaptive Synchronization of Fractional-Order Complex-Valued Neural Networks with Discrete and Distributed Delays
Abstract
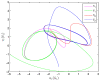
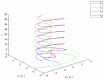
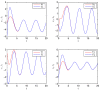
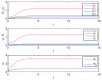
In this paper, the synchronization problem of fractional-order complex-valued neural networks with discrete and distributed delays is investigated. Based on the adaptive control and Lyapunov function theory, some sufficient conditions are derived to ensure the states of two fractional-order complex-valued neural networks with discrete and distributed delays achieve complete synchronization rapidly. Finally, numerical simulations are given to illustrate the effectiveness and feasibility of the theoretical results.
Keywords: complex-valued information; delay; fractional-order; neural networks; synchronization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Existence and finite-time stability of discrete fractional-order complex-valued neural networks with time delays.Neural Netw. 2020 Mar;123:248-260. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.12.012. Epub 2019 Dec 17. Neural Netw. 2020. PMID: 31887685
-
Quasi-projective and complete synchronization of fractional-order complex-valued neural networks with time delays.Neural Netw. 2019 Oct;118:102-109. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2019.06.008. Epub 2019 Jun 20. Neural Netw. 2019. PMID: 31254765
-
Quasi-projective synchronization of fractional-order complex-valued recurrent neural networks.Neural Netw. 2018 Aug;104:104-113. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2018.04.007. Epub 2018 Apr 23. Neural Netw. 2018. PMID: 29753177
-
Adaptive control-based synchronization of discrete-time fractional-order fuzzy neural networks with time-varying delays.Neural Netw. 2023 Nov;168:59-73. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2023.09.019. Epub 2023 Sep 19. Neural Netw. 2023. PMID: 37742532
-
Finite-time cluster synchronization in complex-variable networks with fractional-order and nonlinear coupling.Neural Netw. 2021 Mar;135:212-224. doi: 10.1016/j.neunet.2020.12.015. Epub 2020 Dec 23. Neural Netw. 2021. PMID: 33421899 Review.
Cited by
-
Complex Modified Projective Synchronization of Fractional-Order Complex-Variable Chaotic System with Unknown Complex Parameters.Entropy (Basel). 2019 Apr 17;21(4):407. doi: 10.3390/e21040407. Entropy (Basel). 2019. PMID: 33267121 Free PMC article.
-
Unstable Limit Cycles and Singular Attractors in a Two-Dimensional Memristor-Based Dynamic System.Entropy (Basel). 2019 Apr 19;21(4):415. doi: 10.3390/e21040415. Entropy (Basel). 2019. PMID: 33267129 Free PMC article.
-
Design and Practical Stability of a New Class of Impulsive Fractional-Like Neural Networks.Entropy (Basel). 2020 Mar 15;22(3):337. doi: 10.3390/e22030337. Entropy (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33286111 Free PMC article.
-
Research Frontier in Chaos Theory and Complex Networks.Entropy (Basel). 2018 Sep 25;20(10):734. doi: 10.3390/e20100734. Entropy (Basel). 2018. PMID: 33265823 Free PMC article.
-
On Leader-Following Consensus in Multi-Agent Systems with Discrete Updates at Random Times.Entropy (Basel). 2020 Jun 12;22(6):650. doi: 10.3390/e22060650. Entropy (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33286422 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tu Z.W., Cao J.D., Alsaedi A., Alsaadi F.E., Hayat T. Global lagrange stability of complex-valued neural networks of neutral type with time-varying delays. Complexity. 2016;21:438–450. doi: 10.1002/cplx.21823. - DOI
-
- Gong W.Q., Liang J.L., Cao J.D. Global μ-stability of complex-valued delayed neural networks with leakage delay. Neurocomputing. 2015;168:135–144. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.06.006. - DOI
-
- Song Q.K., Zhao Z.J., Liu Y.R. Stability analysis of complex-valued neural networks with probabilistic time-varying delays. Neurocomputing. 2015;159:96–104. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2015.02.015. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

