Factoid Question Answering with Distant Supervision
- PMID: 33265529
- PMCID: PMC7512957
- DOI: 10.3390/e20060439
Factoid Question Answering with Distant Supervision
Abstract
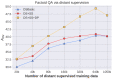
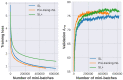
Automatic question answering (QA), which can greatly facilitate the access to information, is an important task in artificial intelligence. Recent years have witnessed the development of QA methods based on deep learning. However, a great amount of data is needed to train deep neural networks, and it is laborious to annotate training data for factoid QA of new domains or languages. In this paper, a distantly supervised method is proposed to automatically generate QA pairs. Additional efforts are paid to let the generated questions reflect the query interests and expression styles of users by exploring the community QA. Specifically, the generated questions are selected according to the estimated probabilities they are asked. Diverse paraphrases of questions are mined from community QA data, considering that the model trained on monotonous synthetic questions is very sensitive to variants of question expressions. Experimental results show that the model solely trained on generated data via the distant supervision and mined paraphrases could answer real-world questions with the accuracy of 49.34%. When limited annotated training data is available, significant improvements could be achieved by incorporating the generated data. An improvement of 1.35 absolute points is still observed on WebQA, a dataset with large-scale annotated training samples.
Keywords: distant supervision; question answering; question paraphrase; reading comprehension.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Adversarial Knowledge Distillation Based Biomedical Factoid Question Answering.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2023 Jan-Feb;20(1):106-118. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2022.3161032. Epub 2023 Feb 3. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 35316189
-
Answering medical questions in Chinese using automatically mined knowledge and deep neural networks: an end-to-end solution.BMC Bioinformatics. 2022 Apr 15;23(1):136. doi: 10.1186/s12859-022-04658-2. BMC Bioinformatics. 2022. PMID: 35428175 Free PMC article.
-
Learning to Answer Visual Questions From Web Videos.IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2025 May;47(5):3202-3218. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2022.3173208. Epub 2025 Apr 8. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell. 2025. PMID: 35533174
-
Question answering systems for health professionals at the point of care-a systematic review.J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2024 Apr 3;31(4):1009-1024. doi: 10.1093/jamia/ocae015. J Am Med Inform Assoc. 2024. PMID: 38366879 Free PMC article.
-
RIL-Contour: a Medical Imaging Dataset Annotation Tool for and with Deep Learning.J Digit Imaging. 2019 Aug;32(4):571-581. doi: 10.1007/s10278-019-00232-0. J Digit Imaging. 2019. PMID: 31089974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berant J., Chou A., Frostig R., Liang P. Semantic Parsing on Freebase from Question-Answer Pairs; Proceedings of the 2013 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing; Seattle, WA, USA. 18–21 October 2013; pp. 1533–1544.
-
- Bordes A., Usunier N., Chopra S., Weston J. Large-scale Simple Question Answering with Memory Networks. arXiv. 2015. 1506.02075
-
- Sun H., Ma H., He X., Yih W.t., Su Y., Yan X. Table Cell Search for Question Answering; Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on World Wide Web; Republic and Canton of Geneva, Switzerland. 11–15 April 2016; pp. 771–782.
-
- Rajpurkar P., Zhang J., Lopyrev K., Liang P. SQuAD: 100,000+ Questions for Machine Comprehension of Text. arXiv. 2016. 1606.05250
-
- Li P., Li W., He Z., Wang X., Cao Y., Zhou J., Xu W. Dataset and Neural Recurrent Sequence Labeling Model for Open-Domain Factoid Question Answering. arXiv. 2016. 1607.06275
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

