Sample Entropy of the Heart Rate Reflects Properties of the System Organization of Behaviour
- PMID: 33265539
- PMCID: PMC7512967
- DOI: 10.3390/e20060449
Sample Entropy of the Heart Rate Reflects Properties of the System Organization of Behaviour
Abstract
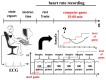
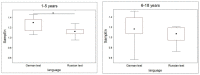
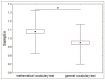
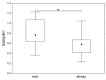
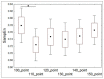
Cardiac activity is involved in the processes of organization of goal-directed behaviour. Each behavioural act is aimed at achieving an adaptive outcome and it is subserved by the actualization of functional systems consisting of elements distributed across the brain and the rest of the body. This paper proposes a system-evolutionary view on the activity of the heart and its variability. We have compared the irregularity of the heart rate, as measured by sample entropy (SampEn), in behaviours that are subserved by functional systems formed at different stages of individual development, which implement organism-environment interactions with different degrees of differentiation. The results have shown that SampEn of the heart rate was higher during performing tasks that included later acquired knowledge (foreign language vs. native language; mathematical vocabulary vs. general vocabulary) and decreased in the stress and alcohol conditions, as well as at the beginning of learning. These results are in line with the hypothesis that irregularity of the heart rate reflects the properties of a set of functional systems subserving current behaviour, with higher irregularity corresponding to later acquired and more complex behaviour.
Keywords: alcohol administration; functional systems; heart rate variability; individual development; irregularity; learning; sample entropy; stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Complexity of heart rate variability during moral judgement of actions and omissions.Heliyon. 2020 Nov 16;6(11):e05394. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05394. eCollection 2020 Nov. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33235931 Free PMC article.
-
Sample entropy of electrocardiographic RR and QT time-series data during rest and exercise.Physiol Meas. 2007 Jun;28(6):731-44. doi: 10.1088/0967-3334/28/6/011. Epub 2007 May 25. Physiol Meas. 2007. PMID: 17664626 Clinical Trial.
-
Complexity quantification of cardiac variability time series using improved sample entropy (I-SampEn).Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2016 Sep;39(3):755-63. doi: 10.1007/s13246-016-0457-7. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med. 2016. PMID: 27305910
-
Hypoglycemia-related electroencephalogram changes assessed by multiscale entropy.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2014 Oct;16(10):688-94. doi: 10.1089/dia.2013.0331. Epub 2014 Jun 3. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24892361 Review.
-
Complexity Change in Cardiovascular Disease.Int J Biol Sci. 2017 Oct 17;13(10):1320-1328. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.19462. eCollection 2017. Int J Biol Sci. 2017. PMID: 29104498 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Longitudinally Tracking Maternal Autonomic Modulation During Normal Pregnancy With Comprehensive Heart Rate Variability Analyses.Front Physiol. 2022 May 9;13:874684. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.874684. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35615673 Free PMC article.
-
Individual-Specific Animated Profiles of Mental Health.Perspect Psychol Sci. 2025 Jul;20(4):787-805. doi: 10.1177/17456916231226308. Epub 2024 Feb 20. Perspect Psychol Sci. 2025. PMID: 38377015 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Maternal Heart Rate Variability and Photoplethysmography Morphology after Corticosteroid Administration: A Prospective, Observational Study.J Clin Med. 2024 Apr 22;13(8):2442. doi: 10.3390/jcm13082442. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 38673715 Free PMC article.
-
Complexity of heart rate variability during moral judgement of actions and omissions.Heliyon. 2020 Nov 16;6(11):e05394. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05394. eCollection 2020 Nov. Heliyon. 2020. PMID: 33235931 Free PMC article.
-
Heart rate dynamics for cognitive load estimation in a driving simulation task.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 30;14(1):31656. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-79728-x. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39738154 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Matheson H.E., Barsalou L.W. Embodiment and Grounding in Cognitive Neuroscience. In: Wixted J.T., Thompson-Schill S.L., editors. Stevens’ Handbook of Experimental Psychology and Cognitive Neuroscience. 4th ed. Volume 3. John Wiley & Sons; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2018. pp. 1–27.
-
- Alexandrov Y.I., Grechenko T.N., Gavrilov V.V., Gorkin A.G., Shevchenko D.G., Grinchenko Y.V., Aleksandrov I.O., Maksimova N.E., Bezdenezhnych B.N., Bodunov M.V. Formation and realization of individual experience: A psychophysiological approach. In: Miller R., Ivanitsky A.M., Balaban P.V., editors. Conceptual Advances in Brain Research. Conceptual Advances in Russian Neuroscience: Complex Brain Functions. Volume 2. Harwood Academic Publishers; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2000. pp. 181–200.
-
- Shvyrkov V.B. Neurophysiological study of animals’ subjective experience. In: John R., Harmony T., editors. Machinery of the Mind. Birkhäuser; Boston, MA, USA: 1990. pp. 337–350.
-
- Alexandrov Y.I. Comparative description of consciousness and emotions in the framework of systemic understanding of behavioural continuum and individual development. In: Teddei-Ferretti C., Musio C., editors. Neuronal Bases and Psychological Aspects of Consciousness, Proceedings of the International School of Biocybernetics, Casamicciola, Napoli, Italy, 13–18 October 1997. Volume 8. World Scientific; New York, NY, USA: 1999. pp. 220–235.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

