Changes in the Physicochemical Properties of Blood and Skin Cell Membranes as a Result of Psoriasis Vulgaris and Psoriatic Arthritis Development
- PMID: 33266237
- PMCID: PMC7731289
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms21239129
Changes in the Physicochemical Properties of Blood and Skin Cell Membranes as a Result of Psoriasis Vulgaris and Psoriatic Arthritis Development
Abstract
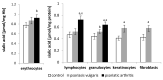
Psoriasis is accompanied by disturbed redox homeostasis, with systemic and local oxidative stress promoting the modification of basic components of cellular membranes. Therefore, the aim of the study was to investigate the effect of development of psoriasis vulgaris and psoriatic arthritis on the composition and physicochemical properties of skin cell membranes (keratinocytes and fibroblasts) and blood cells (lymphocytes, granulocytes and erythrocytes). Both forms of psoriasis are characterized by decreased levels and changes in the localization of membrane phospholipids, and an increased level of sialic acid as well as the lipid peroxidation product (malondialdehyde), which resulted in an increase in the zeta potential of skin cells and blood cells, with granulocytes and lymphocytes affected more than erythrocytes. Using theoretical equations and the dependence of the cell membrane surface charge density as a function of pH, it was shown that patients with psoriatic arthritis have a greater increase in the concentration of negatively charged groups on the membrane surface and reduced the value of the association constant with H+ compared to patients with psoriasis vulgaris. Therefore, it can be suggested that the physicochemical parameters of membranes, skin and blood cells, especially lymphocytes, can be used to assess the severity of the disease.
Keywords: blood cells; electrical properties; membrane composition; psoriasis; skin cells.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
The Differential Effect of Cannabidiol on the Composition and Physicochemical Properties of Keratinocyte and Fibroblast Membranes from Psoriatic Patients and Healthy People.Membranes (Basel). 2021 Feb 4;11(2):111. doi: 10.3390/membranes11020111. Membranes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33557204 Free PMC article.
-
The Immunologic Role of IL-17 in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Pathogenesis.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018 Dec;55(3):379-390. doi: 10.1007/s12016-018-8702-3. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30109481 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Altered Lipid Metabolism in Blood Mononuclear Cells of Psoriatic Patients Indicates Differential Changes in Psoriasis Vulgaris and Psoriatic Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Aug 30;20(17):4249. doi: 10.3390/ijms20174249. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31480263 Free PMC article.
-
New insights into the role of T cells in pathogenesis of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis.Autoimmunity. 2016 Nov;49(7):435-450. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2016.1166214. Epub 2016 Apr 6. Autoimmunity. 2016. PMID: 27050731 Review.
-
Overview of the molecular determinants contributing to the expression of Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis phenotypes.J Cell Mol Med. 2020 Dec;24(23):13554-13563. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.15742. Epub 2020 Oct 31. J Cell Mol Med. 2020. PMID: 33128843 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Cannabidiol and Cannabigerol Modify the Composition and Physicochemical Properties of Keratinocyte Membranes Exposed to UVA.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 4;24(15):12424. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512424. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569799 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying Serum Metabolomic Markers Associated with Skin Disease Activity in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 18;24(20):15299. doi: 10.3390/ijms242015299. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37894979 Free PMC article.
-
Annexin A6 Polymorphism Is Associated with Pro-atherogenic Lipid Profiles and with the Downregulation of Methotrexate on Anti-Atherogenic Lipid Profiles in Psoriasis.J Clin Med. 2022 Nov 29;11(23):7059. doi: 10.3390/jcm11237059. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 36498634 Free PMC article.
-
The Differential Effect of Cannabidiol on the Composition and Physicochemical Properties of Keratinocyte and Fibroblast Membranes from Psoriatic Patients and Healthy People.Membranes (Basel). 2021 Feb 4;11(2):111. doi: 10.3390/membranes11020111. Membranes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33557204 Free PMC article.
-
Causal Association Between Inflammatory Bowel Disease and Psoriasis: A Two-Sample Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study.Front Immunol. 2022 Jun 10;13:916645. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.916645. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35757704 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Merve H.M., Sevilay K., Sibel O., Başak B., Ceren C.G., Demirci T., Cüneyt A. Psoriasis and genetics. Interdiscip. Approach Psoriasis. 2017 doi: 10.5772/intechopen.68344. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

