NO Synthesis Markers are Not Significantly Associated with Blood Pressure and Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Arterial Hypertension: A Cross-Sectional Study
- PMID: 33266290
- PMCID: PMC7760204
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9123895
NO Synthesis Markers are Not Significantly Associated with Blood Pressure and Endothelial Dysfunction in Patients with Arterial Hypertension: A Cross-Sectional Study
Abstract
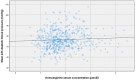
Nitric oxide (NO) synthesis markers, comprising L-homoarginine, asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA), are significantly associated with cardiovascular events and mortality. Being involved in NO pathways, they may be of high importance regulating vascular tone and arterial hypertension, but data on this topic are sparse and controversial. In this study, we evaluated whether these NO synthesis markers are associated with blood pressure values and pulse wave velocity (PWV). This analysis was based on the data of the Styrian Vitamin D Hypertension Trial, which included adults with arterial hypertension. We analyzed correlations of NO synthesis markers with 24 h ambulatory blood pressure values and PWV (primary outcomes), as well as with anthropometric and laboratory data. A total of 509 patients were included in the present analysis. The mean age was 61.2 ± 10.5 years, mean PWV was 8.6 ± 2.4 m/s, mean 24 h systolic blood pressure was 127.5 ± 13.8 mmHg and mean 24 h diastolic blood pressure was 76.4 ± 9.5 mmHg. In bivariate analyses, there was a significant positive correlation between homoarginine and 24 h diastolic blood pressure (r = 0.1; p = 0.02), which was revealed to be no longer significant after adjustment for age, gender and glomerular filtration rate (GFR) in multivariate regression analysis. No other significant correlations of any NO synthesis markers with blood pressure or PWV were observed. In line with previous studies, there were inverse associations between homoarginine and age and between ADMA or SDMA and GFR (p < 0.05 for all). This study did not reveal a significant association between homoarginine, ADMA or SDMA and blood pressure or PWV in hypertensive adults. These results suggested that the associations of these parameters with adverse outcome may not be mediated by hypertension and/or endothelial dysfunction.
Keywords: ADMA; NO; SDMA; arterial hypertension; blood pressure; endothelial dysfunction; homoarginine; pulse wave velocity.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Benjamin E.J., Virani S.S., Callaway C.W., Chamberlain A.M., Chang A.R., Cheng S., Chiuve S.E., Cushman M., Delling F.N., Deo R., et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics-2018 update: A report from the American Heart Association. Circulation. 2018;137:e67–e492. doi: 10.1161/CIR.0000000000000558. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Haghikia A., Yanchev G.R., Kayacelebi A.A., Hanff E., Bledau N., Widera C., Sonnenschein K., Haghikia A., Weissenborn K., Bauersachs J., et al. The role of L-arginine/L-homoarginine/nitric oxide pathway for aortic distensibility and intima-media thickness in stroke patients. Amino Acids. 2017;110:1111–1121. doi: 10.1007/s00726-017-2409-2. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

