Microbiological and Chemical Assessment of Wastewater Discharged by Infiltration Trenches in Fractured and Karstified Limestone (SCA.Re.S. Project 2019-2020)
- PMID: 33266323
- PMCID: PMC7759865
- DOI: 10.3390/pathogens9121010
Microbiological and Chemical Assessment of Wastewater Discharged by Infiltration Trenches in Fractured and Karstified Limestone (SCA.Re.S. Project 2019-2020)
Abstract
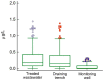
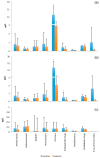
This study investigated the environmental contamination of groundwater as a consequence of the discharge of treated wastewater into the soil. The investigation focused on a wastewater treatment plant located in an area fractured by karst in the Salento peninsula (Apulia, Italy). Water samples were collected at four sites (raw wastewater, treated wastewater, infiltration trench, and monitoring well), monthly from May to December 2019 (with the exception of August), and were tested for (1) panel of bacteria; (2) enteric viruses; and (3) chemical substances. A gradual reduction in the concentration of bacteria, viruses and contaminants of emerging concern was observed across the profile of soil fissured by karst. All monitored bacteria were absent from the monitoring well, except for Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Pepper mild mottle virus and adenovirus were detected at all sampling sites. Personal care products and X-ray contrast media showed the greatest decrease in concentration from infiltration trench to the monitoring well, while the highest residual concentrations in the monitoring well were found for anticonvulsants (78.5%), antimicrobials (41.3%), and antipsychotic drugs (38.6%). Our results show that parameters provided by current law may not always be sufficient to evaluate the sanitary risk relating to the discharge of treated wastewater to the soil.
Keywords: bacteria; contaminants of emerging concern; groundwater; virus; wastewater.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Tijani J.O., Fatoba O.O., Babajide O.O., Petrik L.F. Pharmaceuticals, endocrine disruptors, personal care products, nanomaterials and perfluorinated pollutants: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2016;14:27–49. doi: 10.1007/s10311-015-0537-z. - DOI
-
- Murgolo S., Yargeau V., Gerbasi R., Visentin F., El Habra N., Ricco G., Lacchetti I., Carere M., Curri M.L., Mascolo G. A new supported TiO2 film deposited on stainless steel for the photocatalytic degradation of contaminants of emerging concern. Chem. Eng. J. 2017;318:103–111. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.05.125. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

