Progress in the Applications of Smart Piezoelectric Materials for Medical Devices
- PMID: 33266424
- PMCID: PMC7700596
- DOI: 10.3390/polym12112754
Progress in the Applications of Smart Piezoelectric Materials for Medical Devices
Abstract
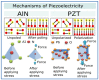
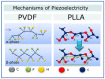
Smart piezoelectric materials are of great interest due to their unique properties. Piezoelectric materials can transform mechanical energy into electricity and vice versa. There are mono and polycrystals (piezoceramics), polymers, and composites in the group of piezoelectric materials. Recent years show progress in the applications of piezoelectric materials in biomedical devices due to their biocompatibility and biodegradability. Medical devices such as actuators and sensors, energy harvesting devices, and active scaffolds for neural tissue engineering are continually explored. Sensors and actuators from piezoelectric materials can convert flow rate, pressure, etc., to generate energy or consume it. This paper consists of using smart materials to design medical devices and provide a greater understanding of the piezoelectric effect in the medical industry presently. A greater understanding of piezoelectricity is necessary regarding the future development and industry challenges.
Keywords: biomedical devices; inorganic materials; organic materials; piezoelectric materials; polymers; smart materials.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Dulnik J., Kołbuk D., Denis P., Sajkiewicz P. The effect of a solvent on cellular response to PCL/gelatin and PCL/collagen electrospun nanofibres. Eur. Polym. J. 2018;104:147–156. doi: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2018.05.010. - DOI
-
- Zaszczyńska A., Sajkiewicz P.Ł., Gradys A., Tymkiewicz R., Urbanek O., Kołbuk D. Influence of process-material conditions on the structure and biological properties of electrospun polyvinylidene fluoride fibers. Bull. Pol. Acad. Sci. Tech. Sci. 2020;68:627–633.
-
- Chen P.J., Saati S., Varma R., Humayun M.S., Tai Y.C. Wireless intraocular pressure sensing using microfabricated minimally invasive flexible-coiled LC sensor implant. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2010;19:721–734. doi: 10.1109/JMEMS.2010.2049825. - DOI
-
- Chen D., Wang J., Xu Y. Highly sensitive lateral field excited piezoelectric film acoustic enzyme biosensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2013;13:2217–2222. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2012.2237508. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources