Rubi Fructus Water Extract Alleviates LPS-Stimulated Macrophage Activation via an ER Stress-Induced Calcium/CHOP Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 33266427
- PMCID: PMC7700618
- DOI: 10.3390/nu12113577
Rubi Fructus Water Extract Alleviates LPS-Stimulated Macrophage Activation via an ER Stress-Induced Calcium/CHOP Signaling Pathway
Abstract
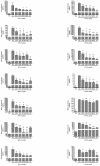
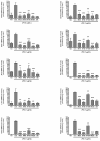
Despite the availability of antibiotics and vaccines, many intractable infectious diseases still threaten human health across the globe. Uncontrolled infections can lead to systemic inflammatory response syndrome and the excessive production of inflammatory cytokines, known as a cytokine storm. As cytokines also play necessary and positive roles in fighting infections, it is important to identify nontoxic and anti-inflammatory natural products that can modulate cytokine production caused by infections. Rubi Fructus, the unripe fruits of Rubus coreanus Miquel, are known to possess antioxidative properties. In this study, the effect of the water extract of Rubi Fructus (RF) on the lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced inflammatory response in RAW 264.7 macrophages was investigated using biochemical and cell biology techniques. Our data indicated that RF inhibits p38 phosphorylation, intracellular calcium release, and the production of nitric oxide (NO), interleukin (IL)-6, monocyte chemotactic activating factor (MCP)-1, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, leukemia inhibitory factor (LIF), lipopolysaccharide-induced CXC chemokine (LIX), granulocyte-colony stimulating factor (G-CSF), granulocyte macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)-1α, MIP-1β, MIP-2, and regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted (RANTES) in LPS-treated macrophages. In addition, we observed decreasing mRNA expression of Chop, Camk2a, Stat1, Stat3, Jak2, Fas, c-Jun, c-Fos, Nos2, and Ptgs2 without cytotoxic effects. We concluded that RF demonstrated immunoregulatory activity on LPS-stimulated macrophages via an endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress-induced calcium/CCAAT-enhancer-binding protein homologous protein (CHOP) pathway and the Janus kinase (JAK)/signal transducers and activators of transcription (STAT) pathway.
Keywords: ER stress; Rubi Fructus; Rubus coreanus; STAT; calcium; chop; cytokine; lipopolysaccharide; macrophage; nitric oxide.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study, in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data, in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
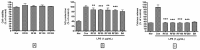


Similar articles
-
Baicalin Modulates Inflammatory Response of Macrophages Activated by LPS via Calcium-CHOP Pathway.Cells. 2022 Sep 30;11(19):3076. doi: 10.3390/cells11193076. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36231038 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Angelica sinensis (Oliv.) Diels Water Extract on RAW 264.7 Induced with Lipopolysaccharide.Nutrients. 2018 May 21;10(5):647. doi: 10.3390/nu10050647. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 29883374 Free PMC article.
-
Moutan Cortex Extract Modulates Macrophage Activation via Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Calcium Signaling and ER Stress-CHOP Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 20;24(3):2062. doi: 10.3390/ijms24032062. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36768384 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage polarization and function with emphasis on the evolving roles of coordinated regulation of cellular signaling pathways.Cell Signal. 2014 Feb;26(2):192-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 9. Cell Signal. 2014. PMID: 24219909 Review.
-
Decoding cell death signals in liver inflammation.J Hepatol. 2013 Sep;59(3):583-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2013.03.033. Epub 2013 Apr 6. J Hepatol. 2013. PMID: 23567086 Review.
Cited by
-
Inhibitory Effect of Luteolin on Spike S1 Glycoprotein-Induced Inflammation in THP-1 Cells via the ER Stress-Inducing Calcium/CHOP/MAPK Pathway.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Oct 20;17(10):1402. doi: 10.3390/ph17101402. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39459041 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophages in Renal Injury, Repair, Fibrosis Following Acute Kidney Injury and Targeted Therapy.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 13;13:934299. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.934299. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35911736 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of Cytoskeleton, Protein Trafficking, and Signaling Pathways by Metabolites from Cucurbitaceae, Ericaceae, and Rosaceae Plant Families.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Nov 10;15(11):1380. doi: 10.3390/ph15111380. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36355554 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An exhaustive examination of the research progress in identifying potential JAK inhibitors from natural products: a comprehensive overview.Chin Med. 2025 Aug 21;20(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s13020-025-01176-0. Chin Med. 2025. PMID: 40841966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Baicalin Modulates Inflammatory Response of Macrophages Activated by LPS via Calcium-CHOP Pathway.Cells. 2022 Sep 30;11(19):3076. doi: 10.3390/cells11193076. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36231038 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

