Effectiveness of Active Therapy-Based Training to Improve the Balance in Patients with Fibromyalgia: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 33266511
- PMCID: PMC7700277
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm9113771
Effectiveness of Active Therapy-Based Training to Improve the Balance in Patients with Fibromyalgia: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Balance impairment is a frequent disorder in patients with fibromyalgia (FMS), increasing the risk of falls and decreasing physical function and quality of life. In recent years, the use of active therapy-based training (ATBT) has increased, with the aim of improving balance in women with FMS. Our study aimed to assess the effect of ATBT to improve different balance outcomes in subjects with FMS. A systematic review with meta-analysis was carried out. We searched PubMed Medline, SCOPUS, Web of Science, CINAHL, and PEDro (Physiotherapy Evidence Database) databases up to September 2020. We included randomized controlled trials (RCT) that assessed the balance in patients with FMS after ATBT and compared to other treatments or no intervention. In a random-effects model, the standardized mean difference (SMD) was used to calculate the effect size. Ten studies were included in the review providing data from 546 FMS patients with a mean age of 52.41 ± 2.90 years old (98% females). Our results showed a medium effect favors ATBT with respect to other therapies for monopedal static balance (SMD = 0.571; 95% CI = 0.305, 0.836; p < 0.001), dynamic balance (SMD = 0.618; 95% CI = 0.348, 0.888; p < 0.001), and functional balance (SMD = 0.409; 95% CI = 0.044, 0.774; p = 0.028). No statistically significant differences were found for balance on unstable support. The present meta-analysis showed moderate-quality evidence of a medium effect of ATBT to improve dynamic and functional balance and low-quality evidence of a medium effect to improve monopedal static balance with respect to other therapies or no intervention.
Keywords: active therapy; chronic fatigue syndrome; fibromyalgia; meta-analysis; postural balance; postural sensory organization.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
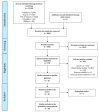



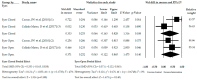
References
-
- Mas A., Carmona L., Valverde M., Ribas B., EPISER Study Group Prevalence and impact of fibromyalgia on function and quality of life in individuals from the general population: Results from a nationwide study in Spain. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2008;26:519–526. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

