Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia: A Focus on Thrombosis
- PMID: 33267665
- PMCID: PMC7769912
- DOI: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.120.315445
Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia: A Focus on Thrombosis
Abstract
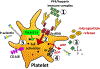
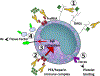
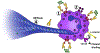
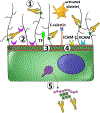
Heparin-induced thrombocytopenia is an immune-mediated disorder caused by antibodies that recognize complexes of platelet factor 4 and heparin. Thrombosis is a central and unpredictable feature of this syndrome. Despite optimal management, disease morbidity and mortality from thrombosis remain high. The hypercoagulable state in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia is biologically distinct from other thrombophilic disorders in that clinical complications are directly attributable to circulating ultra-large immune complexes. In some individuals, ultra-large immune complexes elicit unchecked cellular procoagulant responses that culminate in thrombosis. To date, the clinical and biologic risk factors associated with thrombotic risk in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia remain elusive. This review will summarize our current understanding of thrombosis in heparin-induced thrombocytopenia with attention to its clinical features, cellular mechanisms, and its management.
Keywords: antibodies; heparin; platelets; thrombocytopenia; thrombosis.
Figures
References
-
- Kuter DJ, Konkle BA, Hamza TH, et al. Clinical outcomes in a cohort of patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Am J Hematol. 2017;92:730–738 - PubMed
-
- Gruel Y, Vayne C, Rollin J, et al. Comparative analysis of a French prospective series of 144 patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (FRIGTIH) and the literature. Thromb Haemost. 2020;120:1096–1107 - PubMed
-
- Elalamy I, Tardy-Poncet B, Mulot A, de Maistre E, Pouplard C, Nguyen P, Cleret B, Gruel Y, Lecompte T, Tardy B, Group GHS. Risk factors for unfavorable clinical outcome in patients with documented heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. Thromb Res. 2009;124:554–559 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

