High prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among symptomatic healthcare workers in a large university tertiary hospital in São Paulo, Brazil
- PMID: 33267836
- PMCID: PMC7709093
- DOI: 10.1186/s12879-020-05662-8
High prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among symptomatic healthcare workers in a large university tertiary hospital in São Paulo, Brazil
Abstract
Background: Brazil became the epicenter of the COVID-19 pandemic in Latin America since May 2020, reporting the highest number of cases and deaths in the region. Healthcare workers (HCWs) are at increased risk of SARS-CoV-2 infection, experiencing a significant burden from COVID-19. Identifying and understanding the clinical characteristics and risk factors associated with infection are of paramount importance to inform screening strategies and infection control practices in this scenario. The aims of this study were to investigate the prevalence and clinical characteristics of HCWs with COVID-19 symptoms.
Methods: Between March 21st and May 22nd, 2020 a cross-sectional study was performed in a tertiary university hospital in São Paulo. Prevalence of SARS-CoV-2 infection among HCWs with COVID-19 symptoms was determined by RT-PCR testing on nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal samples. Participants were asked to complete an electronic structured questionnaire including clinical and demographic data.
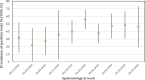
Results: Overall, 125 (42.37%) of 295 symptomatic HCWs tested positive for SARS-CoV-2. Over the 10-week study period, positivity rates varied from 22.2% (95% CI 15.9-60.3%) in the second week to 55.9% (95% CI 43.2-68.6%) in the sixth week, reaching a plateau (38-46%) thereafter. Median (SD) age was 34.2 (9.9) years and 205 (69.5%) were female. We did not find significant differences in the prevalence of the most commonly reported underlying medical condition among healthcare workers that tested positive or negative for SARS-CoV-2 infection. After multivariable analysis, using logistic regression, anosmia (adjusted OR 4.4 95% CI 2.21-8.74) and ocular pain (adjusted OR 1.95 95% CI 1.14-3.33) were the only symptoms independently associated with positivity for SARS-CoV-2 infection. Follow-up information on clinical outcomes showed that 9 (7.2%) HCWs were hospitalized (seven were male) and 2 (1.6%) died.
Conclusions: The findings of this study confirmed the high burden of SARS-CoV-2 infection among healthcare workers in the hardest hit city by the pandemic in Latin America. Anosmia and ocular pain were symptoms independently associated with COVID-19 diagnosis. In low and middle-income countries, where limited availability of tests is frequent, these findings may contribute to optimize a targeted symptom-oriented screening strategy.
Keywords: COVID-19; Epidemiology; Health care workers; Risk factors; SARS-CoV-2.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization (WHO). Coronavirus disease (COVID-2019). Weekly Epidemiological and Operational updates October 2020. https://www.who.int/emergencies/diseases/novel-coronavirus-2019/situatio.... (Accessed 02 Oct 2020).
-
- Ministry of Health of Brazil. Coronavirus disease case panel 2019- COVID19 in Brazil. https://covid.saude.gov.br. (Accessed 02 Oct 2020).
-
- Word Health Organization (WHO) Summary table of SARS cases by country, 1 November 2002–7 August 2003. 2020.
-
- Kluytmans-van den Bergh MFQ, Buiting AGM, Pas SD, Bentvelsen R, van den Bijllaardt W, Oudheusden AJG, et al. Prevalence and clinical presentation of health care workers with symptoms of coronavirus disease 2019 in 2 Dutch Hospitals during an early phase of the pandemic. JAMA Netw Open. 2020;3(5):e209673. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2020.9673. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Olgueira MD; Munoz-Ruiperez C; Alonso-Lopez MA; Delgado R. SARS-CoV-2 infection in health care workers in a large public hospital in Madrid, Spain, during March 2020. medRxiv 2020.04.07.20055723; doi: 10.1101/2020.04.07.20055723.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous