Interplay between endoplasmic reticulum stress and non-coding RNAs in cancer
- PMID: 33267910
- PMCID: PMC7709275
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-020-01002-0
Interplay between endoplasmic reticulum stress and non-coding RNAs in cancer
Abstract
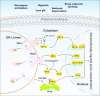
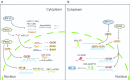
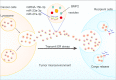
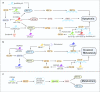
To survive, cancer cells are subjected to various internal and external adverse factors, including genetic mutations, hypoxia, nutritional deficiencies, and drug toxicity. All of these factors result in the accumulation of unfolded proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum, which leads to a condition termed endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress) and triggers the unfolded protein response (UPR). UPR downstream components strictly control transcription and translation reprogramming to ensure selective gene expression, including that of non-coding RNA (ncRNAs), to adapt to adverse environments. NcRNAs, including microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), and circular RNAs (circRNAs), play important roles in regulating target gene expression and protein translation, and their aberrant expression is related to tumor development. Dysregulation of ncRNAs is involved in the regulation of various cellular characteristics of cancer cells, including growth, apoptosis, metastasis, angiogenesis, drug sensitivity, and tumor stem cell properties. Notably, ncRNAs and ER stress can regulate each other and collaborate to determine the fate of tumor cells. Therefore, investigating the interaction between ER stress and ncRNAs is crucial for developing effective cancer treatment and prevention strategies. In this review, we summarize the ER stress-triggered UPR signaling pathways involved in carcinogenesis followed by the mutual regulation of ER stress and ncRNAs in cancer, which provide further insights into the understanding of tumorigenesis and therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: Cancer; ER stress; Interplay; UPR; ncRNAs.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Crosstalk between endoplasmic reticulum stress and non-coding RNAs in cardiovascular diseases.Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023 Jul-Aug;14(4):e1767. doi: 10.1002/wrna.1767. Epub 2022 Nov 24. Wiley Interdiscip Rev RNA. 2023. PMID: 36420580 Review.
-
The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress in the regulation of long noncoding RNAs in cancer.J Cell Physiol. 2022 Oct;237(10):3752-3767. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30846. Epub 2022 Aug 12. J Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35959643 Review.
-
Decoding contextual crosstalk: revealing distinct interactions between non-coding RNAs and unfolded protein response in breast cancer.Cancer Cell Int. 2024 Mar 11;24(1):104. doi: 10.1186/s12935-024-03296-3. Cancer Cell Int. 2024. PMID: 38468244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA and ER stress in cancer.Semin Cancer Biol. 2021 Oct;75:3-14. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2020.12.025. Epub 2021 Jan 7. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021. PMID: 33422566 Review.
-
Long non-coding RNA-mediated modulation of endoplasmic reticulum stress under pathological conditions.J Cell Mol Med. 2024 Jul;28(14):e18561. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.18561. J Cell Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39072992 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Noncoding RNAs as sensors of tumor microenvironmental stress.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022 Jul 16;41(1):224. doi: 10.1186/s13046-022-02433-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 35842651 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Composite Bioinformatic Analysis to Explore Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress-Related Prognostic Marker and Potential Pathogenic Mechanisms in Glioma by Integrating Multiomics Data.J Oncol. 2022 Oct 4;2022:9886044. doi: 10.1155/2022/9886044. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36245971 Free PMC article.
-
Long noncoding RNA Gm2694 drives depressive-like behaviors in male mice by interacting with GRP78 to disrupt endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis.Sci Adv. 2022 Dec 2;8(48):eabn2496. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abn2496. Epub 2022 Dec 2. Sci Adv. 2022. PMID: 36459549 Free PMC article.
-
LINP1 represses unfolded protein response by directly inhibiting eIF2α phosphorylation to promote cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023 Mar 14;12(1):31. doi: 10.1186/s40164-023-00395-1. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36918934 Free PMC article.
-
A miR-770-5p/XBP1-driven pathway controls ESR1 expression and tamoxifen response in luminal breast cancer.Mol Biol Rep. 2025 May 23;52(1):496. doi: 10.1007/s11033-025-10598-w. Mol Biol Rep. 2025. PMID: 40407833
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

